Figure 1.
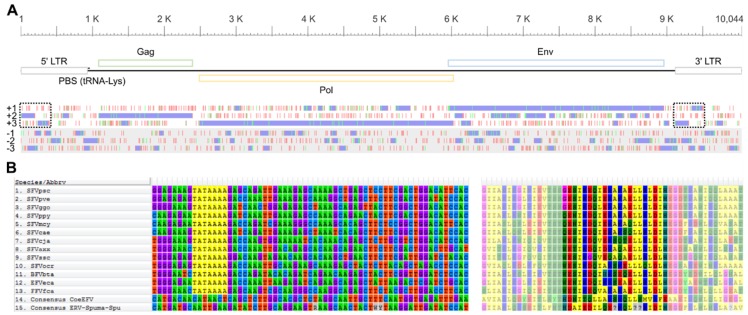
Reconstructed, putative, ERV-Spuma-Spu genome (A) and foamy virus (FV) internal promoters (B). Top-A, scale bar indicates nucleotide position. Middle-A, schematic diagram representing the genomic organisation of ERV-Spuma-Spu. LTR: long terminal repeat (grey); PBS: primer binging site; Gag: group antigen gene (green); Pol: polymerase gene (yellow); Env: envelope gene (blue). Bottom-A, start (green) and stop (red) codon positions in the six translation frames (+1, +2, +3, −1, −2, and −3). Potential open reading frames are shown in purple. The dotted boxes indicate the two open reading frames identified as a single accessory gene in [8]. The nucleotide sequences of consensus ERV-Spuma-Spu can be found in Figure S1 and Data S3. Left-B, internal promoters (TATAAAA) towards the 3’ end of the env gene could be identified in all mammalian FVs (highlighted in yellow) but were absent from CoeEFV (endogenous FVs) and ERV-Spuma-Spu. Right-B, protein sequences used to guide the nucleotide alignment. Those corresponding to the sequences on the left are shown in brighter colors.