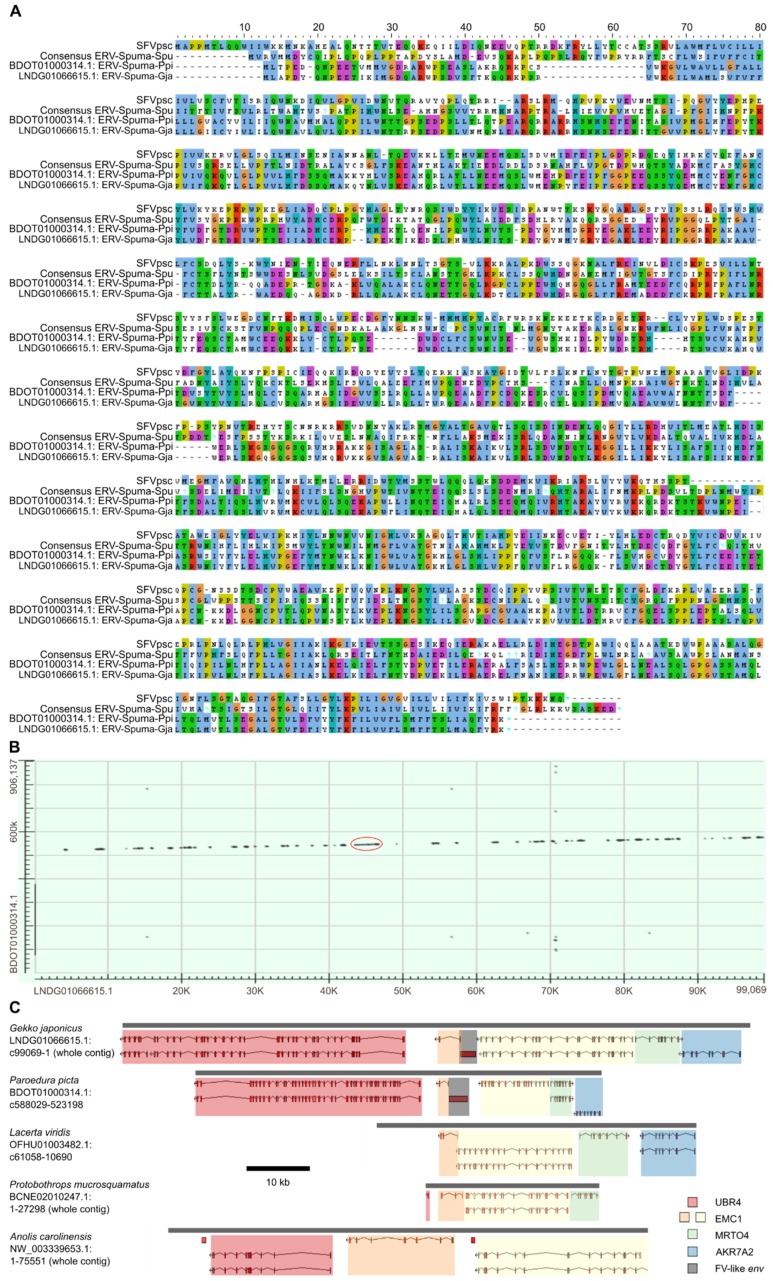
Figure 2.
FV-like env sequences in panther gecko (Paroedura picta, BDOT01000314.1) and Schlegel’s Japanese gecko (Gekko japonicus, LNDG01066615.1). (A) Alignment of Env protein sequences of prototype FV (SFVpsc), consensus ERV-Spuma-Spu, and the two gecko FV-like endogenous viral elements, BDOT01000314.1: ERV-Spuma-Ppi, and LNDG01066615.1: ERV-Spuma-Gja. (B) BLASTn dot matrix between LNDG01066615.1 and BDOT01000314.1. The red circle indicates the location of the FV-like env sequences. (C) Homologous regions in three other reptiles, namely European green lizard (Lacerta viridis, OFHU01003482.1), brown spotted pitviper (Protobothrops mucrosquamatus, BCNE02010247.1), and green anole (Anolis carolinensis, NW_003339653.1). Genes were predicted by AUGUSTUS [9]. Four eukaryotic genes are shown on the diagram from left to right: ubiquitin protein ligase E3 component n-recognin 4 (UBR4, red), ER membrane protein complex subunit 1 (EMC1, orange and yellow), MRT4 homolog, ribosome maturation factor (MRTO4, green), and aldo-keto reductase family 7 member A2 (AKR7A2, blue). Gene homology at the protein level was examined by using BLASTp. FV-like env genes are highlighted in grey. Grey bars represent the contigs, and the scale bar (black) represents a length of 10 kb.