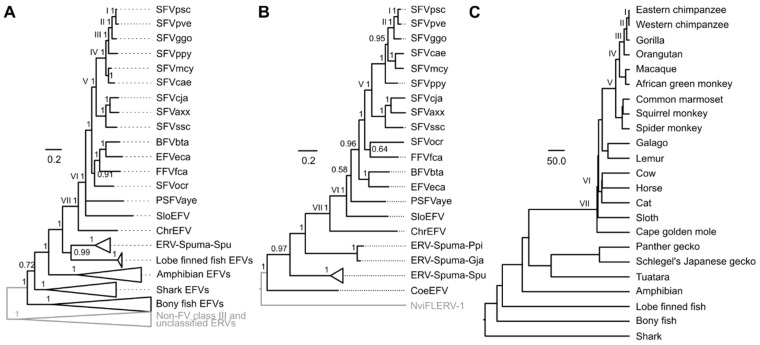
Figure 3.
Foamy virus Pol, Env, and host phylogenies. Bayesian Pol (A) and Env (B) phylogenies were estimated by using MrBayes 3.2.6 [13], and their scale bars are in the units of amino acid substitutions per site. Both Pol and Env trees were rooted by the mid-point rooting method, and the determined outgroups are shown in grey. Arabic numerals on nodes are Bayesian posterior probability clade support values. The topologies of the Pol and the Env trees were compared to that of the host phylogeny (C) to identify virus–host co-speciation events labeled with Roman numerals. Nodes on different phylogenies that are labeled with the same Roman numeral are those corresponding to the same co-speciation event. The timescale of the identified co-speciation nodes, directly inferred from their hosts (Table S5), was used to calibrate the timescales of other nodes. The host tree topology was estimated elsewhere [26], and its scale bar is in units of millions of years. The virus–host association can be found in Table S6. SFV: simian foamy virus; psc, Pan troglodytes schweinfurthii chimpanzee; pve, Pan troglodytes verus chimpanzee; ggo, Gorilla gorilla gorilla; ppy, Pongo pygmaeus orangutan; mcy, Macaca cyclopis macaque; cae, Chlorocebus aethiops Grivet; cja, Callithrix jacchus marmoset; axx, Ateles spider monkey; scc, Saimiri sciureus squirrel monkey; ocr, Otolemur crassicaudatus brown greater galago; BFVbta, bovine foamy virus Bos taurus; EFVeca, equine foamy virus Equus caballus; FFVfca, feline foamy virus Felis catus; PSFVaye, prosimian foamy virus aye-aye; EFV, endogenous foamy virus; SloEFV, sloth EFV; ChrEFV, Cape golden mole EFV; CoeEFV, Coelacanth EFV; NviFLERV-1, Notophthalmus viridescens foamy virus-like endogenous retrovirus - 1.