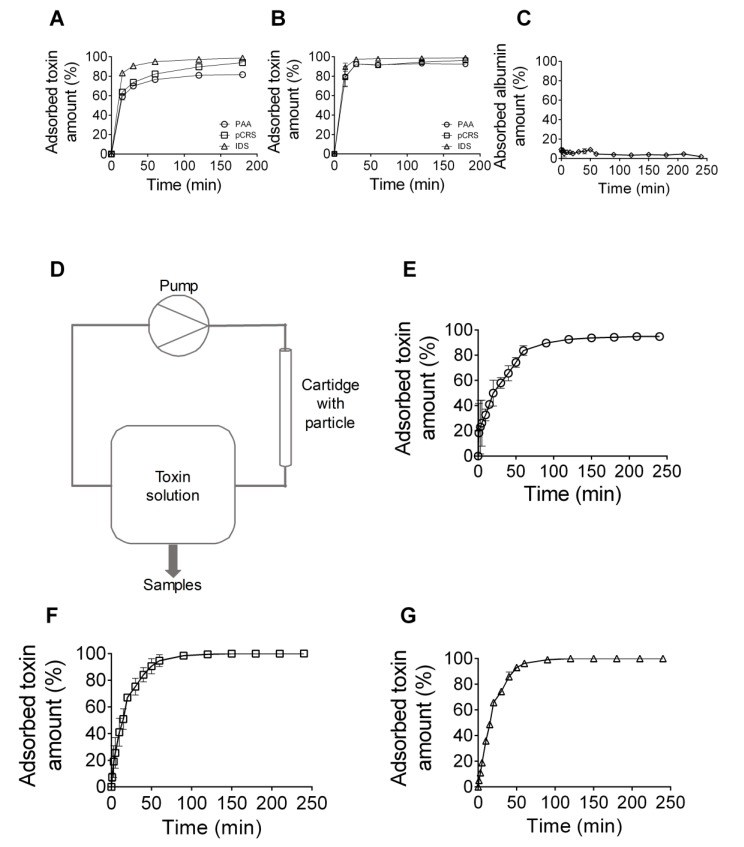
Figure 3.
Quantification of the binding capacity of the newly developed adsorber particle to hydrophobic, protein-bound uremic toxins. The particles were incubated with the uremic toxins phenylacetic acid (PAA), p-cresyl sulfate (pCRS), and indoxyl sulfate (IDS), and their adsorption capacities were quantified by reversed-phase chromatography. (A,B) Quantification of the adsorption capacity after static incubation of the adsorber particles with the uremic toxins dissolved in BSA solution (A) or in blood (B) for different incubation periods, as indicated. Shown are mean values ± S.E.M of three independent experiments. (C) Quantification of the protein concentration of a BSA solution after static incubation with the adsorber particles. Shown are mean values ± S.E.M of four independent experiments. (D) Flowchart of the experimental set-up for the quantification of uremic toxin adsorption to adsorber particles in conditions of flow. (E–G) Quantification of the adsorption capacity after flow incubation of the adsorber particles with phenylacetic acid (PAA) (E), p-cresyl sulfate (pCRS) (F), or indoxyl sulfate (IDS) (G), all dissolved in PBS, and after different time points, as indicated. Shown are mean values ± S.E.M of three independent experiments.