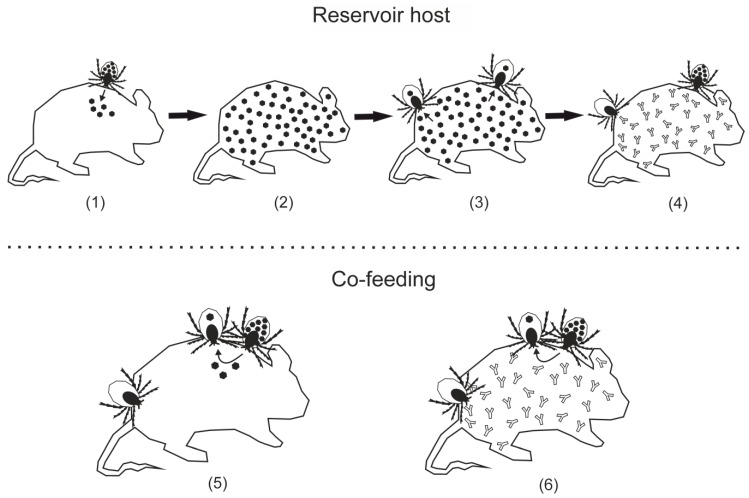
Figure 2.
TBEV reservoir hosts: Small mammals, especially rodents, are considered to be reservoir hosts for TBEV. Infected ticks transmit the virus ( ) to the animal host (1), leading to viremia (2). Naïve ticks acquire TBEV by consuming the blood of a viremic host (3). As soon as viremia comes to an end, this route of transmission is blocked by circulating antibodies (
) to the animal host (1), leading to viremia (2). Naïve ticks acquire TBEV by consuming the blood of a viremic host (3). As soon as viremia comes to an end, this route of transmission is blocked by circulating antibodies ( ) (4). Co-feeding enables ticks to pass TBEV among themselves without the need for a viremic host. When naïve ticks feed in close proximity with an infected tick, the animal host acts as a transmission bridge (5). This can take place even when the host has antibodies against TBEV (6).
) (4). Co-feeding enables ticks to pass TBEV among themselves without the need for a viremic host. When naïve ticks feed in close proximity with an infected tick, the animal host acts as a transmission bridge (5). This can take place even when the host has antibodies against TBEV (6).