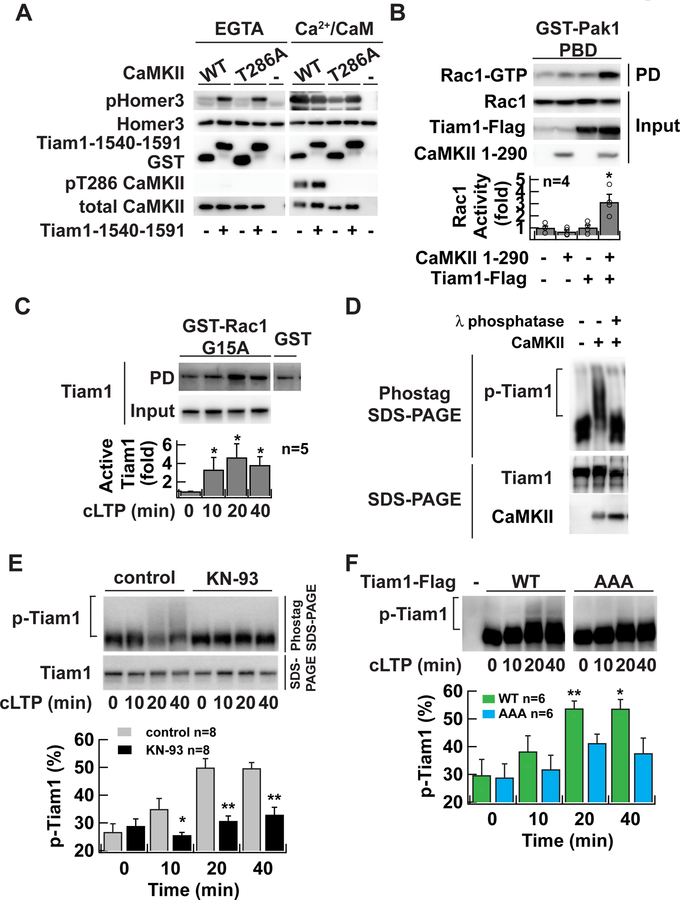
Figure 5. RAKEC formation between CaMKII and Tiam1 is required for Tiam1 phosphorylation during LTP.
A. In vitro kinase assay of Tiam1-bound CaMKII. CaMKII was affinity-purified with a Flag antibody from HEK293T cells expressing Flag-tagged CaMKII and incubated with GST-Tiam1 fragment (residue 1540–1591) or GST in the presence of Ca2+/calmodulin to form a complex. Then EGTA was added to chelate Ca2+. ATP was omitted in these steps to avoid autophosphorylation. In vitro phosphorylation reaction was carried out in the absence (EGTA) or presence of Ca2+/calmodulin (Ca2+/CaM) using purified GST-Homer3 as a substrate after adding ATP. The reaction products were subjected to western blotting with antibodies against phosphorylated-Homer3 (pHomer3) (Mizutani et al., 2008), GST, T286 phosphorylated CaMKII (pT286 CaMKII), and CaMKII.
B. Activation of Tiam1 by CaMKII. Tiam1 was coexpressed with a constitutively active form of CaMKII (1–290) in HEK293T cells. Activated Rac1 was pulled down with Pak1-p21-bindingdomain, which specifically binds to the GTP-bound form of Rac1. *, p < 0.05, compared to nontransfected cells; t-test.
C. Persistent activation of Tiam1 RacGEF after chemical LTP induction in neurons in dissociated culture demonstrated by Rac1-G15A pull-down assay. Activated Tiam1 in the lysate of neurons underwent glycine stimulation and were subject to a pull-down assay using a nucleotide-free Rac1 G15A mutant, which selectively binds to activated RacGEFs. Bound Tiam1 was detected by western blotting with anti-Tiam1 antibody. *, p < 0.05, compared to non-stimulated neurons; Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
D. Phos-tag SDS-PAGE analysis of Tiam1 protein. Tiam1-Flag proteins were purified from transfected HEK293T cells with Flag-agarose and incubated with Mg2+/ATP, and 20 nM of CaMKII. The samples were treated with 10 U of λ phosphatase for 60 min at 30 °C. Samples were resolved either 7.5 µM Phos-tag SDS-PAGE (top) or conventional SDS-PAGE (bottom). Tiam1 and CaMKII proteins were detected by western blotting with anti-Tiam1 or CaMKII antibodies, respectively. Slowly migrating species represent phosphorylated proteins. The reason why shifted band does not form a discrete ladder is likely because of the existence of multiple phosphorylation sites on Tiam1.
E. Persistent phosphorylation of Tiam1 after chemical LTP induction in neurons in dissociated culture. Lysate from neurons which underwent chemical LTP induction with glycine for 10 min in the absence or presence of CaMKII inhibitor KN-93 (10 µM) were subject to Phos-tag SDS-PAGE to separate phosphorylated protein from unphosphorylated protein on a gel and then blotted with anti-Tiam1 antibody. Lower blot is a conventional SDS-PAGE. *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01, compared to control; one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey’s HSD post-hoc test.
F. The persistent phosphorylation requires Tiam1/CaMKII complex formation. Flag-tagged Tiam1 (wild-type or AAA mutant) was introduced into neurons in dissociated culture using a lentiviral vector. Phosphorylated Tiam1 was detected similarly to E. except that anti-Flag antibody was used. *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01, compared to non-stimulated WT; one-way ANOVA with the Dunnett’s post-hoc test comparisons.
Representative blots are shown from at least three independent experiments in A and D. Data are represented as mean ± SEM (B, C, E, F).
See also Figure S4.