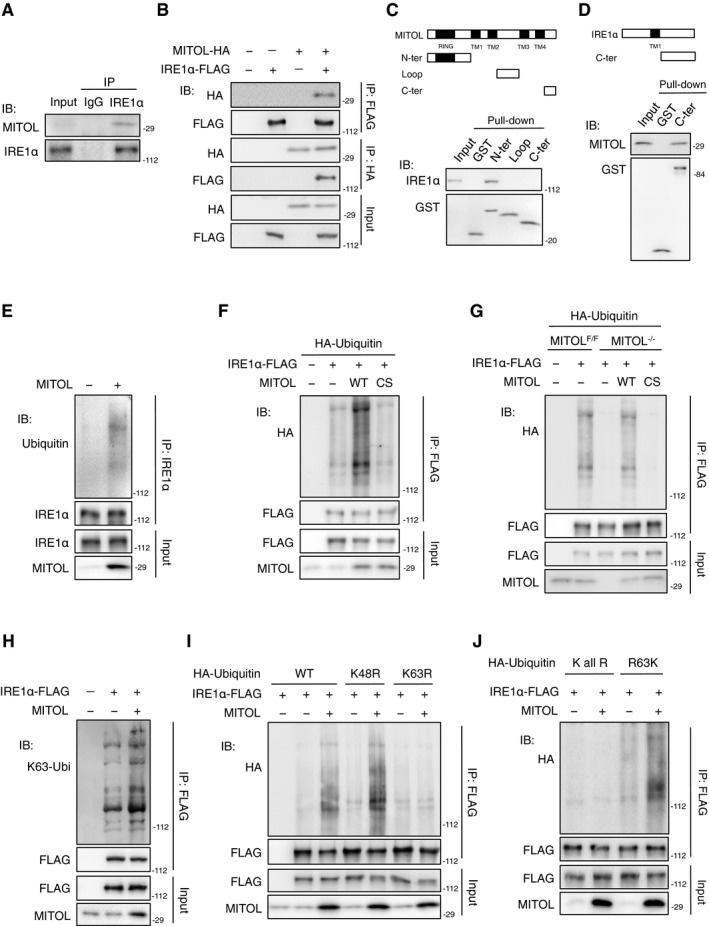
Figure 4. MITOL interacts with and ubiquitylates IRE1α.
-
A–DInteraction between MITOL and IRE1α. Lysates of HEK293 cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti‐IRE1α antibody, followed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies (A). Lysates of HEK293 cells co‐transfected with indicated vectors were subjected to immunoprecipitation, followed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies (B). GST pull‐down assay of IRE1α or MITOL was performed on lysates of MEFs, followed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies (C, D). N‐ter: 1–90 aa of MITOL; Loop: 158–210 aa of MITOL; C‐ter: 241–278 aa of MITOL, 465–977 aa of IRE1α.
-
E–GMITOL ubiquitylated IRE1α. Lysates of HEK293 cells (E, F) or MEFs (G) transfected with indicated vectors were immunoprecipitated with indicated antibody, followed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies.
-
H–JMITOL adds lysine 63‐linked polyubiquitin chains to IRE1α. Lysates of HEK293 cells transfected with indicated vectors were immunoprecipitated with indicated antibody. IRE1α ubiquitylation was detected as similar to (E). WT: wild‐type ubiquitin. K48R, K63R: ubiquitin mutants containing lysine (K)‐to‐arginine (R) substitution at position 48 or 63, respectively. K all R: ubiquitin mutant containing all lysine‐to‐arginine substitutions. R63K: ubiquitin mutants containing only one lysine intact at position 63.
