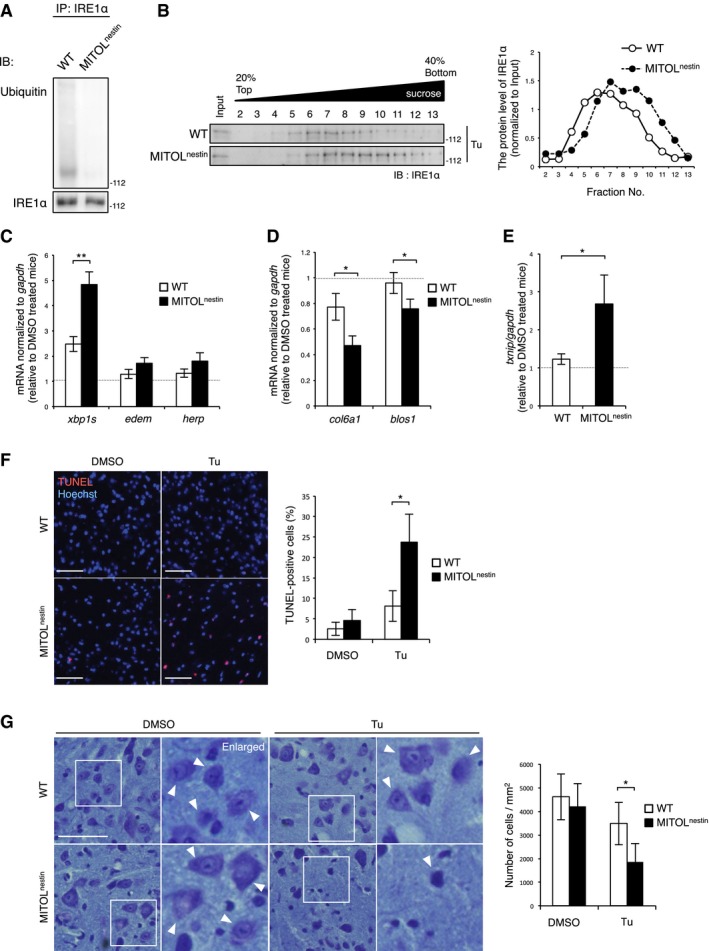
Figure 7. IRE1α hyper‐activation accompanying with apoptosis in the MITOL‐KO spinal cord under ER stress.
-
AMITOL ubiquitylated IRE1α in the spinal cord of mice. Lysates of the spinal cord in mice were immunoprecipitated with anti‐IRE1α antibody, followed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. WT: MITOLF/F mice; MITOLnestin: MITOLF/F, Nestin‐Cre mice.
-
BLoss of MITOL led to hyper‐oligomerization of IRE1α in the spinal cord under ER stress. Three‐month‐old WT or MITOLnestin mice were treated with 1 mg/kg Tu for 24 h. Spinal cord was solubilized with NP‐40 lysis buffer and separated by sucrose density‐gradient centrifugation.
-
C–EMITOL deletion resulted in hyper‐activation of IRE1α RNase in ER stress. WT or MITOLnestin mice were injected with Tu for 24 h, and spinal cord was analyzed by qRT–PCR. Error bars represent SD (n = 3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (Student's t‐test).
-
F, GIncreased ER stress‐induced apoptosis in the MITOL‐KO spinal cord. Three‐month‐old WT or MITOLnestin mice were treated with Tu for 24 h, and each spinal cord was stained using TUNEL and Hoechst (F) or cresyl violet (G). The right panels show twofold magnification images of the boxed regions. Arrowheads indicate the representative neurons. Scale bar represents 50 μm (F) or 20 μm (G). Error bars represent SD (n = 3). *P < 0.05 (Student's t‐test).
