Figure 1.
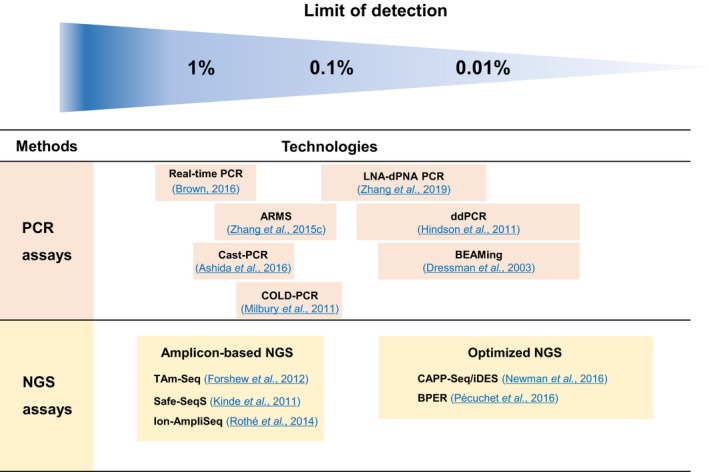
Examples of technology platforms for detecting circulating tumor DNA and limit of detection ranges. These depend on number of mutations measured and quantity of DNA present in a blood sample. Optimized NGS techniques provide sequencing error correction. Other ctDNA assays being applied to pancreatic cancer include personalized panels and commercially available tests. PCR: polymerase chain reaction; NGS: next‐generation sequencing; ARMS: amplification‐refractory mutation system; COLD‐PCR: coamplification at lower denaturation temperature PCR; Cast‐PCR: competitive allele‐specific TaqMan PCR; LNA‐dPNA PCR: locked nucleic acid‐dual peptide nucleic acid PCR clamp; ddPCR: droplet digital PCR; BEAMing: beads, emulsion, amplification, and magnetics digital PCR; TAm‐Seq: tagged‐amplicon deep sequencing; CAPP‐Seq/iDES: cancer personalized profiling by deep sequencing with integrated digital error suppression; BPER: base‐position error rate.
