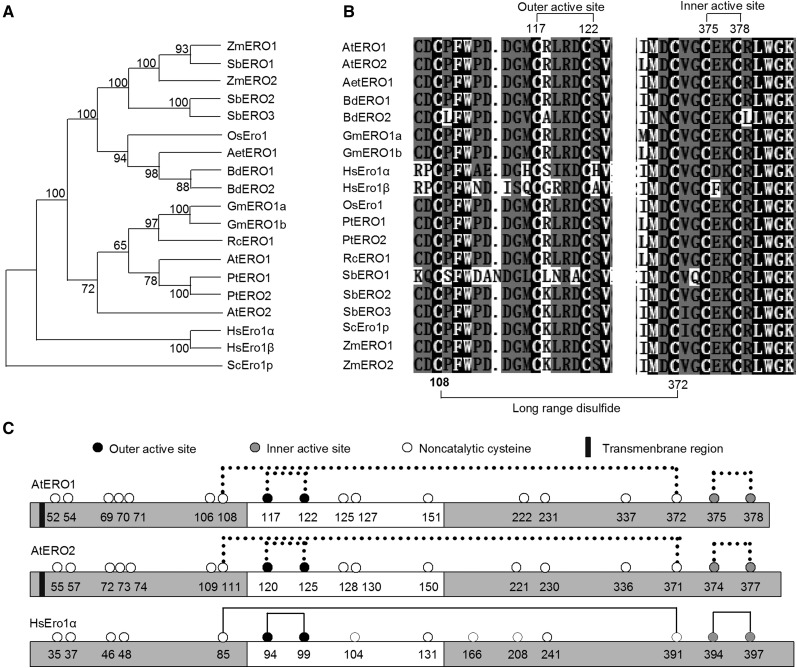
Figure 1.
Analysis of Ero1s from different species. A, Phylogenetic analysis of Ero1s from different species. A neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree was constructed using MEGA 7.0. software based on putative amino acid sequences of various Ero1 homologs. Bootstrap values are indicated at each tree root. The amino acid sequence of yeast Ero1p was used as an outgroup. Aet, Aegilops tauschii; At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Bd, Brachypodium distachyon; Gm, Glycine max; Hs, Homo sapiens; Os, Oryza sativa; Pt, Populus trichocarpa; Rc, Ricinus communis; Sb, Sorghum bicolor; Sc, Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Zm, Zea mays. B, Amino acid sequence alignment of Ero1 regions containing the outer/inner active sites from various species. Amino acid sequences of Ero1 proteins from various species were aligned using the ClustalW program. White-on-black letters indicate amino acid residues conserved in all sequences analyzed. Long-range disulfide bonds and active sites in Arabidopsis Ero1s are indicated. C, Schematic representation of AtERO1, AtERO2, and HsEro1α. Lines indicate disulfide bonds. The flexible loop region is represented by the white bars. Dotted lines indicate the putative disulfide bonds based on the results of amino acid sequence alignment of Ero1 homologs.