Figure 1.
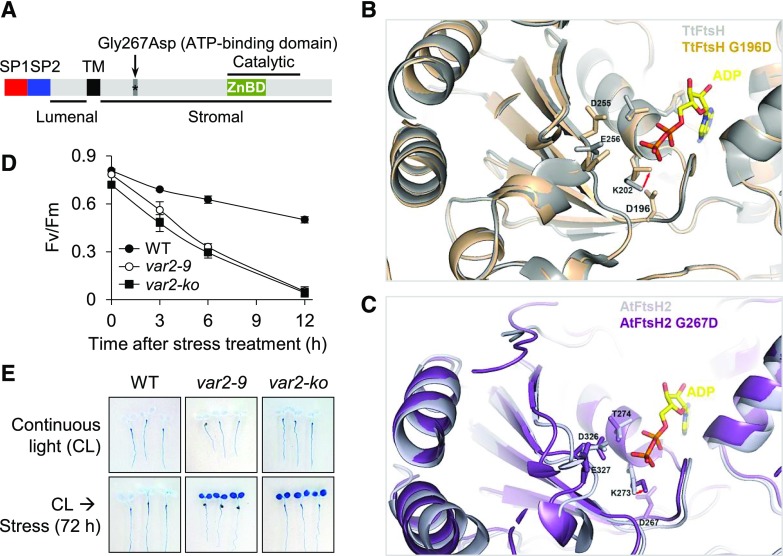
var2-9 and var2-ko seedlings are susceptible to photooxidative stress. A, Schematic illustration of FtsH2 and the missense mutation in var2-9. The mutant form of FtsH2 in the var2-9 allele contains a missense mutation (Gly-267-Asp) in the ATP-binding domain. SP1 and SP2 are the two signal peptides that are responsible for targeting to the chloroplast and the thylakoid membrane, respectively. TM marks the transmembrane domain, and Catalytic indicates the catalytic domain, which contains a Zn-binding domain. Lumenal and Stromal indicate different sides of the FtsH2 topology. B, The possible effect of G267D on ATP binding was analyzed using the known structure of TtFtsH (Protein Data Bank identifier 4EIW) as a template. The G267 in AtFtsH2 is equivalent to the G196 in TtFtsH. The residues K202, T203, D255, and E256 are known to be involved in the interaction with ATP. The TtFtsH and TtFtsHG196D structures are colored in gray and orange, respectively. The G196D mutation induces a conformational change of K202 because of steric hindrance, indicated by the red arrow. C, The AtFtsH2 structure is modeled using that of TtFtsH as a template. The residues K273, T274, D326, and E327 are likely to be involved in ATP binding in AtFtsH2. The AtFtsH2 and AtFtsH2G267D structures are colored in light purple and purple, respectively. AtFtsH2G267D may interfere with the ATP binding similar to that in TtFtsHG196D, indicated by the red arrow. Protein structures were visualized with PyMol (pymol.org). D, Time-course analysis of the rate of PSII damage. Five-day-old var2-9, var2-ko, and wild-type (WT) seedlings initially grown under CL (40 μmol m−2 s−1 at 22°C ± 2°C) were subjected to photoinhibitory (300 μmol m−2 s−1 at 10°C ± 2°C) conditions. The PSII activity (Fv/Fm) was determined at the indicated time points. At least 20 seedlings per genotype were used for each measurement. Error bars indicate sd. E, After 72 h of light stress treatment, the degree of cell death in the different genotypes was visualized by staining whole seedlings with Trypan Blue. Seedlings that were grown under nonstressful light (CL) were used as a control (top row).