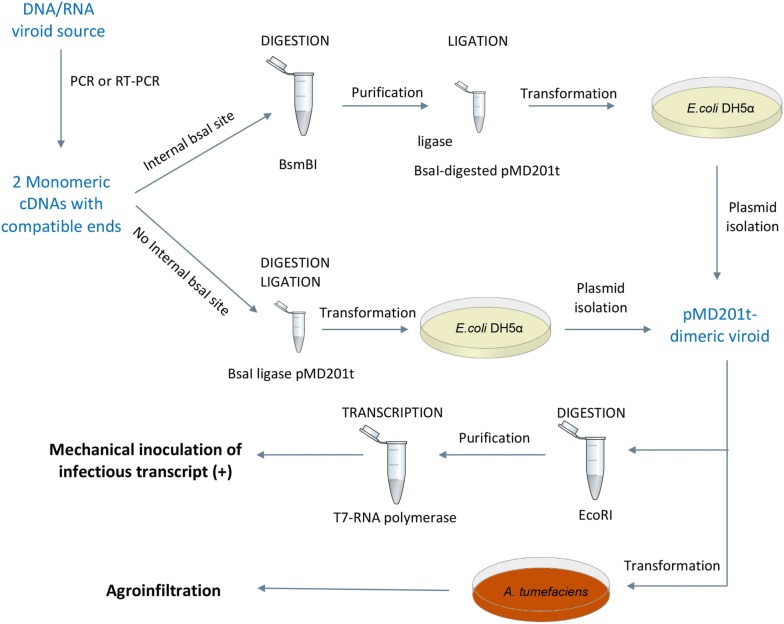
Fig. 2.
Workflow proposed to obtain infectious clones of a viroid. Viroid sequence can be amplified from infected tissue by RT-PCR or from a DNA source by PCR. If the viroid sequence does not contain a bsaI recognition site, the viroidal cDNA can be directly assembled into the binary vector (pMD201t), replacing a lethal gene, in a simultaneous bsaI restriction and ligation. Conversely, if there the viroid contains a bsaI recognition site, it can be cloned using another IIs enzyme, such as BsmBI. Once digested and purified, the viroid cDNA is dimerized by ligation to a previously digested pMD201t. The dimeric viroidal cDNA cloned into pMD201t (pMD201t-viroid) can be used to generate the infectious RNA transcript in vitro, using T7 RNA polymerase onto a linearized plasmid (digested with EcoRI). Additionally, the pMD201t-viroid can be transformed into Agrobacterium tumefaciens for transient plant transformation and subsequent production of infective RNA in vivo