Figure 5.
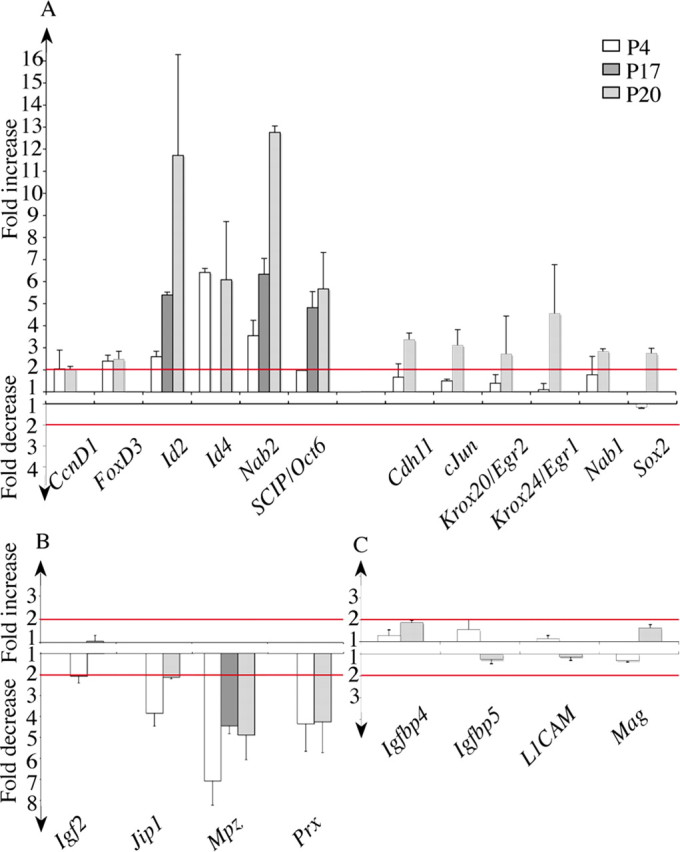
The myelination defect correlates with abnormal levels of expression of several genes involved in Schwann cell differentiation or proliferation. The mRNA levels were determined by RT-PCR analysis on samples of sciatic nerves at P4, P17, and P20. The graphs show the ratios of mRNA levels in homozygous mutant versus wild-type animals, presented as fold increase or decrease. A, The expression of a first subset of genes is increased in mutant compared with wild-type animals. The ratios superior to the threshold of twofold (indicated by the top red line) were considered significant. B, For a second subset of genes, the expression is decreased in mutant compared with wild-type animals. The ratios superior to the threshold of twofold (indicated by the lower red line) were considered significant. C, A last subset of genes showed only limited variations in expression. Error bars indicate SEM.
