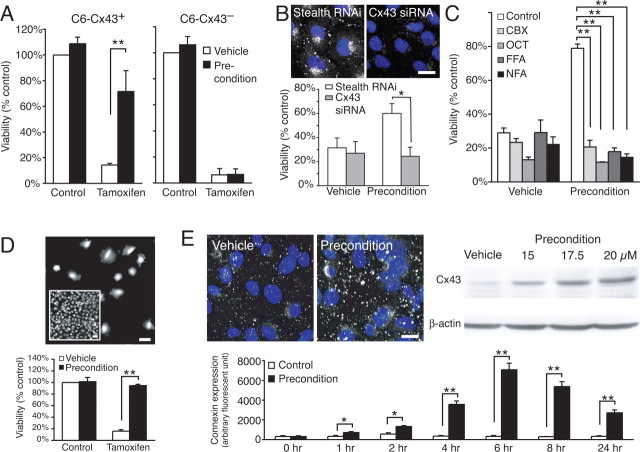
Figure 2.
Cx43 expression is required for preconditioning of C6 cells. A, Comparison of preconditioning stimulation of C6–Cx43+ and C6–Cx43− cells (preconditioning exposure to tamoxifen, 17.5 μm; lethal exposure, 35 μm, respectively). Data represent average ± SE (n = 3–4). **p < 0.01, Tukey–Kramer test. B, Reduced Cx43 expression in C6–Cx43+ cells by siRNA abrogated the protection afforded by precondition. Top shows Cx43 immunoreactivity (white) with DAPI (blue) in cultures treated with Stealth RNAi and Cx43 siRNA in parallel. Scale bar, 13 μm. Data represent average ± SE (n = 4–5). *p < 0.05, Tukey–Kramer test. C, Several Cx channel inhibitors, including carbenoxolone (CBX; 100 μm), octanol (OCT; 500 μm), flufenamic acid (FFA; 100 μm), and niflemic acid (NFA; 100 μm), attenuated the increased resistance after preconditioning. Data represent average ± SE (n = 6–9). **p < 0.01, Tukey–Kramer test. D, Top, A low-density culture of C6–Cx43+ that is devoid of cell–cell contact as opposed to the confluent culture (inset). Scale bars, 50 μm. Bottom, Precondition-afforded resistance does not require cell–cell contact. Data represent average ± SE (n = 4–14). **p < 0.01, Tukey–Kramer test. E, Top left, Cx43 immunolabeling (white) increased after preconditioning (tamoxifen). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 50 μm. Top right, Dose-dependent increase of Cx43 protein after exposure to sublethal concentrations of tamoxifen. Bottom, Comparison of relative changes in Cx43 immunolabeling (white) as a function of time after exposure to vehicle and preconditioning (20 μm tamoxifen). Scale bar, 10 μm. Data represent average ± SE (n = 4). **p < 0.01, Tukey–Kramer test.