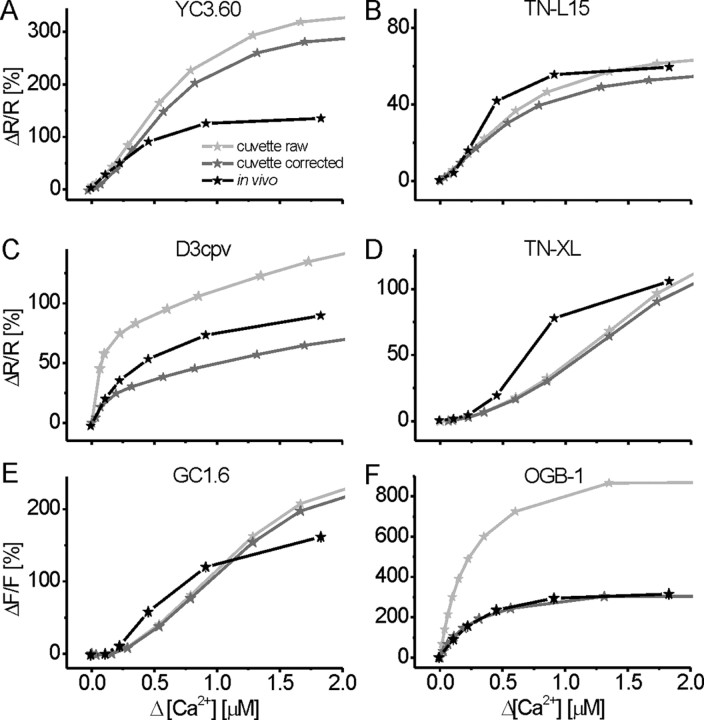
Figure 4.
In vivo versus in vitro: quantitative comparison of fractional fluorescence changes of GECIs and OGB-1 at steady state. GECI and OGB-1 fluorescence changes were analyzed at the end of stimulus trains in presynaptic boutons of transgenic larvae (black traces) and compared with the purified protein and OGB-1 in solution in the cuvette. A, YC3.60; B, TN-L15; C, D3cpv; D, TN-XL; E, GC1.6; F, OGB-1. Fractional fluorescence changes (ΔR/R and ΔF/F) in vivo (black traces) are compared with in vitro ΔR/R and ΔF/F calculated from spectrophotometer data either directly (light gray traces) or after applying corrections (dark gray traces; see Materials and Methods). Correction was done for the resting calcium concentration and the width of the bandpass filters in the detection pathway of the 2PLSM. Both corrections significantly reduce Fmax, which is most obvious for the synthetic indicator OGB-1 (F). Applying these corrections, the fluorescence change of OGB-1 in vivo matches perfectly the one observed in vitro. All GECIs show significant deviations of in vivo from in vitro (A–E), the origin of which remains to be investigated. However, the applied corrections cancel out effects of the applied imaging conditions, and the remaining differences between GECIs probably represent interactions with the chemical environment.