Figure 4.
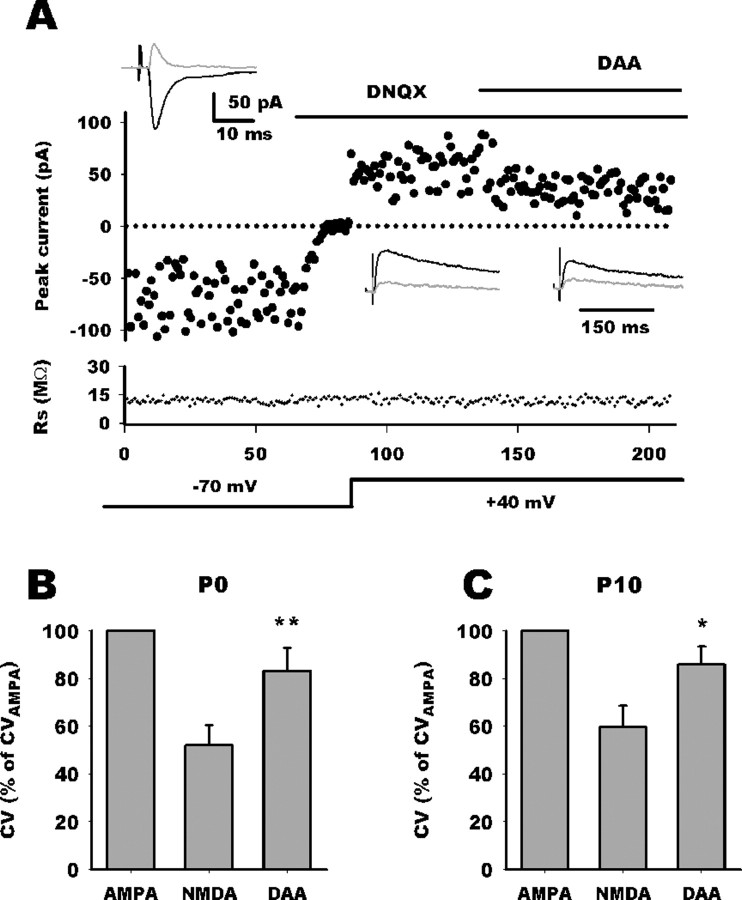
Competitive NMDA antagonist selectively restores CV. A, Comparison of EPSC variance mediated by AMPARs and NMDARs. EPSC amplitudes are plotted against stimulus number with holding potential and application of DNQX and d-AA indicated schematically. Access resistance magnitude is plotted against stimulus number. Top black traces represent average traces in the different conditions, and the gray traces are SDs. For this P0 neuron, CVAMPA was 0.6 and CVNMDA was 0.35. Application of d-AA decreased NMDA current and increased CV to 0.42. B, C, Bar histograms summarizing d-AA effect on CVNMDA relative to CVAMPA at P0 and P10 in group 1 neurons. For neurons whose CVNMDA was smaller than CVAMPA, application of d-AA nearly restored CVNMDA (DAA) to control values. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.