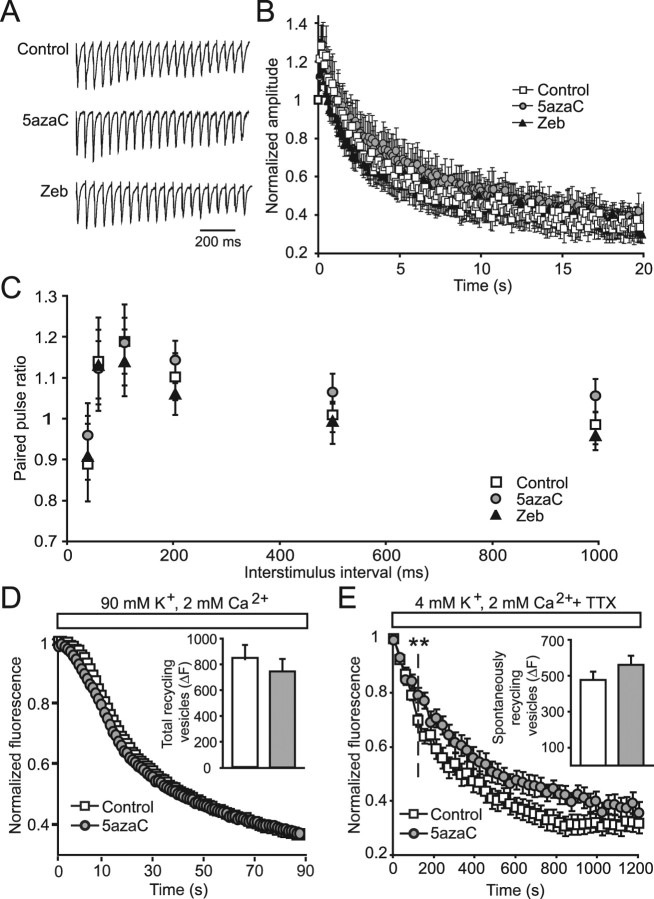
Figure 2.
DNMT inhibition for 24 h specifically affects spontaneous presynaptic function. A, Normalized sample traces of the first 20 evoked EPSCs, recorded in the presence of PTX, in response to 10 Hz field stimulation from neurons treated with inhibitors of DNMTs. B, Average normalized EPSC amplitudes from treated neurons measured during 20 s of 10 Hz stimulation show no alterations in response depression after treatment with DNMT inhibitors compared with controls (control, n = 15; 5azaC, n = 14; Zeb, n = 12). C, Paired-pulse ratios of the first two evoked EPSCs in response to various stimulation frequencies were not significantly different in DNMT inhibitor-treated neurons compared with controls. D, Total synaptic vesicle pools were loaded with FM1-43 by 47 mm K+-induced depolarization and destained using 90 mm K+. The kinetics of destaining was not different between control and 5azaC-treated neurons. Inset, The bar graph depicts no change in total recycling synaptic vesicles from control and 5azaC-treated synapses measured by the total change in fluorescence during 90 mm K+ destaining (control, n = 8 coverslips; 5azaC, n = 8 coverslips). E, Spontaneously recycling synaptic vesicles were loaded for 15 min in the presence of TTX and destained for 20 min in the same manner. Destaining of spontaneous vesicles was slower in 5azaC-treated synapses compared with controls (**p < 0.01). Inset, The bar graph indicates no difference in the numbers of spontaneously recycling synaptic vesicles between control and DNMT inhibitor-treated neurons (control, n = 6; 5azaC, n = 5).