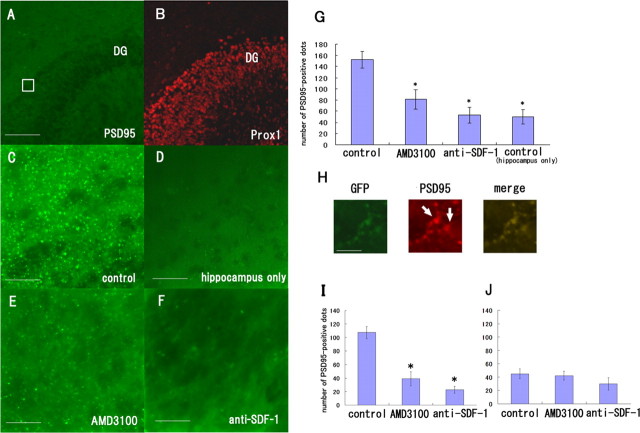
Figure 7.
SDF-1α is necessary for synapse formation between the perforant fibers and the DG neurons. A, Slices of the EC and hippocampus were obtained from the rats at postnatal days 0–1 and were incubated for 9 d in the absence (A–C) or presence of 50 μg/ml AMD3100 (E) or 60 μg/ml anti-SDF-1 antibody (F). D, The hippocampal slices were cultured in the absence of the EC slices. The tissues were stained with the anti-PSD95 (green) and anti-Prox1 antibodies (red). C, PSD-95-positive signals were observed between the perforant fibers and the DG. D, The PSD-95-positive signals were considerably fewer in the hippocampal slices cultured in the absence of EC slices than in the coculture of the EC and hippocampus. E, F, Treatment with AMD3100 or the anti-SDF-1 antibody resulted in a decrease in the number of PSD-95-positive signals. G, The number of PSD-95-positive signals in the DG was measured and quantified. H, The hippocampal slices were obtained from wild-type rats and the EC slices were from GFP transgenic rats. The tissues were stained with the anti-PSD95 (red) and anti-GFP antibodies (green). The PSD-95-positive signals contacted with the GFP-positive perforant fibers. I, The number of PSD-95-positive signals that contacted with the perforant fibers was measured and quantified. J, The number of PSD-95-positive signals that did not contact with the perforant fibers was measured and quantified. G, I, J, The data are represented as the mean ± SEM of four samples of each group (5 different fields of 100 μm2 area for each sample). The asterisks (*) indicate statistical significance (p < 0.05) (two-way ANOVA followed by Scheffé's multiple-comparison test). Scale bars: A, B, 100 μm; C–F, 25 μm; H, 12 μm.