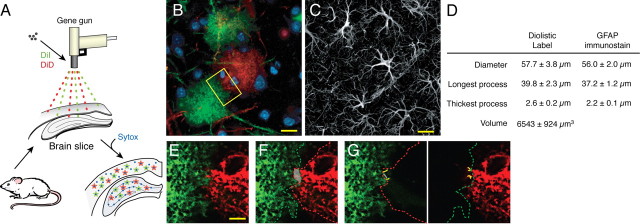
Figure 1.
Cortical astrocytes are organized in nonoverlapping domains. A, Schematic of the procedure used for diolistic labeling of lightly fixed brain slices with DiI (green) and DiD (red). B, Representative labeling of cortical astrocytes with DiI and one with DiD. DiI and DiD distribute evenly in the plasma membrane of single astrocytes and outline their bushy structure in a control mouse. Scale bar (SB), 20 μm. C, Immunostaining against GFAP in cortex. Only the cell body and major processes of cortical astrocytes are GFAP positive. SB, 20 μm. D, Morphometric analysis of cortical astrocytes based on diolistic labeling and GFAP immunostaining (mean ± SEM). E, High-power image of box in B. SB, 10 μm. F, Area of overlap between two neighboring astrocytes is delineated in gray. The red line indicates the border of the domain of the DiD-labeled astrocyte (red), whereas the green line indicates the border of the domain of the DiI-labeled astrocyte (green). G, Yellow lines highlight the processes that extend into their neighbor's domain.