Figure 5.
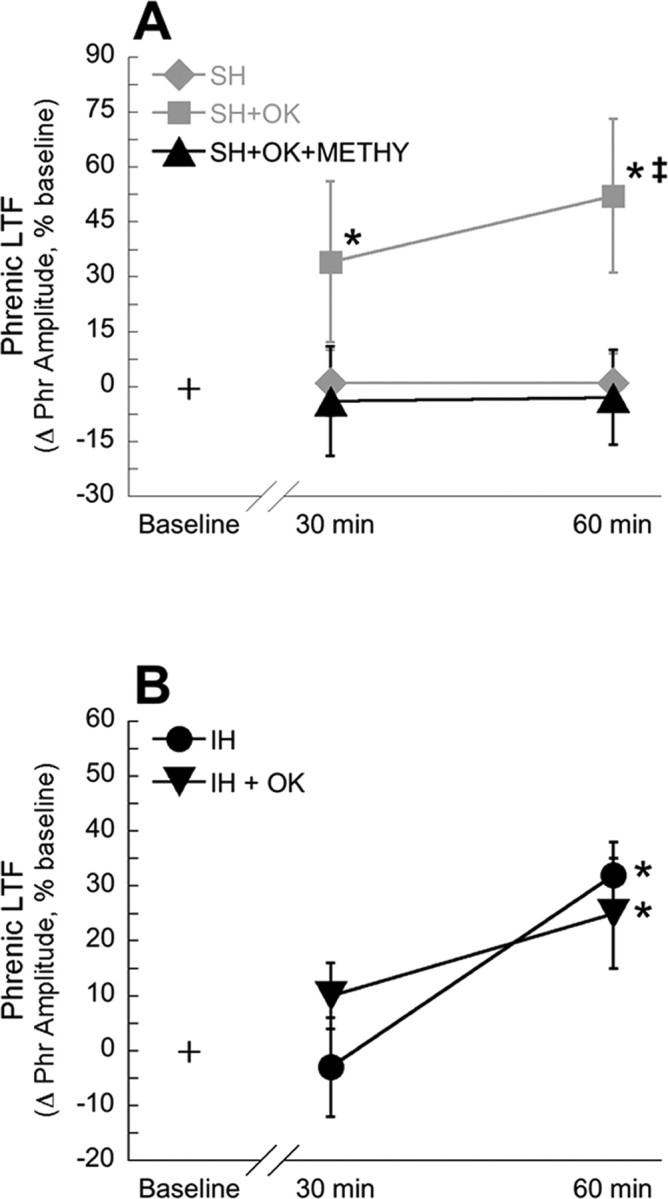
pLTF may be caused by similar mechanisms in rats treated with intermittent hypoxia or sustained hypoxia with concomitant protein phosphatase inhibition. A, Inhibition of serotonin receptors with methysergide abolishes pLTF in rats treated with intrathecal okadaic acid and sustained hypoxia (SH+OK+METHY; ▴). For comparison, data for rats treated with intrathecal aCSF and SH (♦) or 25 nm okadaic acid and sustained hypoxia (SH+OK; ■) are recapitulated from Figure 4. B, Okadaic acid does not alter pLTF in rats treated with intermittent hypoxia. Rats treated with intrathecal aCSF and IH (•) or 25 nm okadaic acid and intermittent hypoxia (IH + OK; ▾) showed increased phrenic burst amplitude after hypoxia, indicating pLTF. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of the change in phrenic burst amplitude as a percentage of baseline. *Significantly increased from baseline (p < 0.05). ‡Significantly increased relative to rats treated with okadaic acid, sustained hypoxia, and methysergide (p < 0.05).
