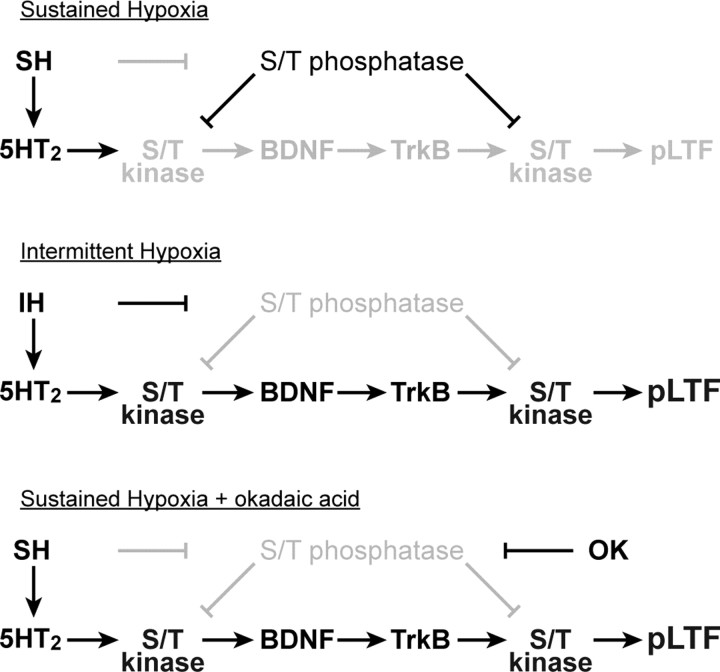
Figure 7.
Sensitivity of pLTF to the pattern of hypoxia: postulated mechanisms. Top, SH induces serotonin release in the phrenic motor nucleus to activate 5-HT2 receptors, but a phosphatase constraint is present, thereby inhibiting the protein kinase cascade that initiates pLTF. Middle, IH induces serotonin release in the phrenic motor nucleus, activating 5-HT2 receptors and suppressing protein phosphatase activity, thus enabling the protein kinase cascade leading to pLTF (protein kinase to BDNF to TrkB to pLTF). Bottom, Sustained hypoxia initiates the serotonergic component of pLTF, and phosphatase activity is suppressed pharmacologically by okadaic acid (OK), thus enabling pLTF expression. Bold letters and symbols indicate activated pathways; faded gray symbols and letters indicate suppressed components of the cellular network. For further explanation, see Discussion.