Figure 2.
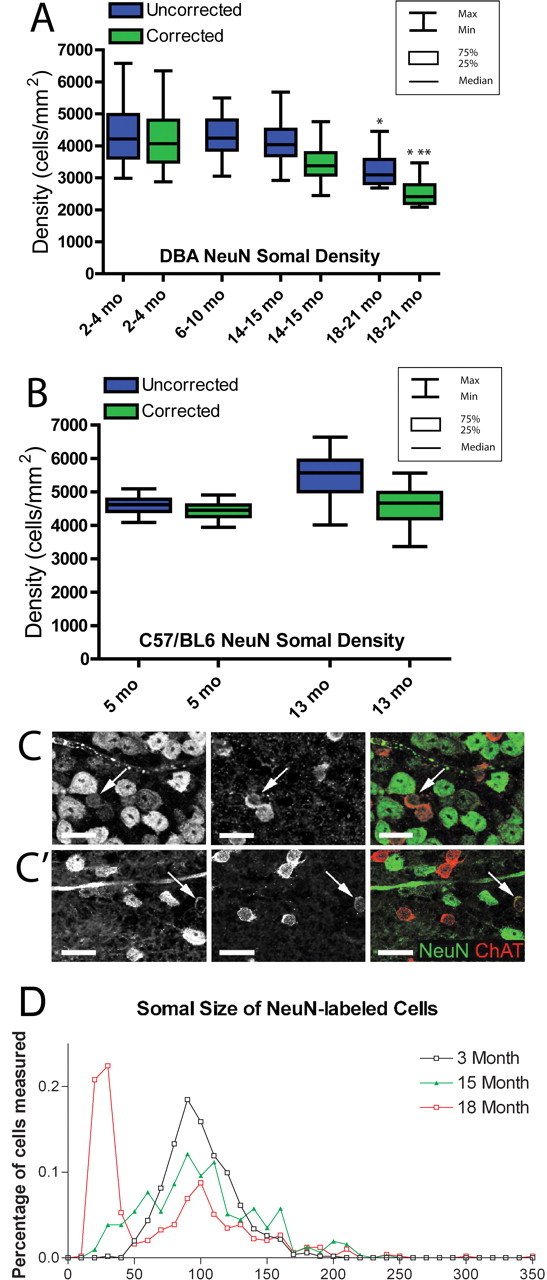
Unbiased stereological cell quantification and somal size measurements to assess RGCs across the disease spectrum of the DBA/2. A, Box plot graph showing the density of NeuN-positive cells in the GCL both before (blue) and after (green) application of the NeuN/ChAT-positive amacrine cell correction factor. NeuN-positive densities (green) include only NeuN-positive RGCs. Boxes extend from the 25th to the 75th percentile, with a line at the median cell density. Error bars show the highest and lowest values. The 2–4 month group has the largest range of NeuN-positive cell density, whereas median density is similar across all age groups until 18–21 months. The oldest group has significantly lower NeuN-positive cell density than all age groups (*p < 0.01). There was no significant difference in corrected NeuN-positive cell density between the 2–4 and 14–15 month groups, and the 18–21 month group had significantly lower corrected NeuN-positive cell density than both of the other corrected age groups. This difference was greater between the 2–4 month group (**p < 0.001) than the 14–15 month group (*p < 0.01). A correction factor was not created for 6–10 month retinas, so this group is represented by total NeuN-positive cells only. B, Box plot graph illustrating NeuN-positive cells in the GCL of C57BL/6 control retinas at 5 and 13 months of age. NeuN-positive cell densities are represented as in A. There is no significant difference in corrected NeuN-positive RGC density (p > 0.1). C, C′, Immunolabeling for NeuN and ChAT in DBA/2 whole-mount retina at 3 (C) and 18 (C′) months illustrating a visible reduction in both number and size of NeuN-positive cells by 18 months. Arrows indicate amacrine cells with both NeuN and ChAT immunofluorescence. Scale bar, 20 μm. D, Histogram of NeuN-positive somal area as measured from retinal whole mounts at 3, 15, and 18 months. The 3 month retinas have nearly 20% NeuN-positive cells with a somal area ∼100 μm2; this percentage decreased with age. From 15–18 months, there is a significant increase in the number of NeuN-positive cells with somal areas <50 μm2 (p < 0.05).
