Figure 7.
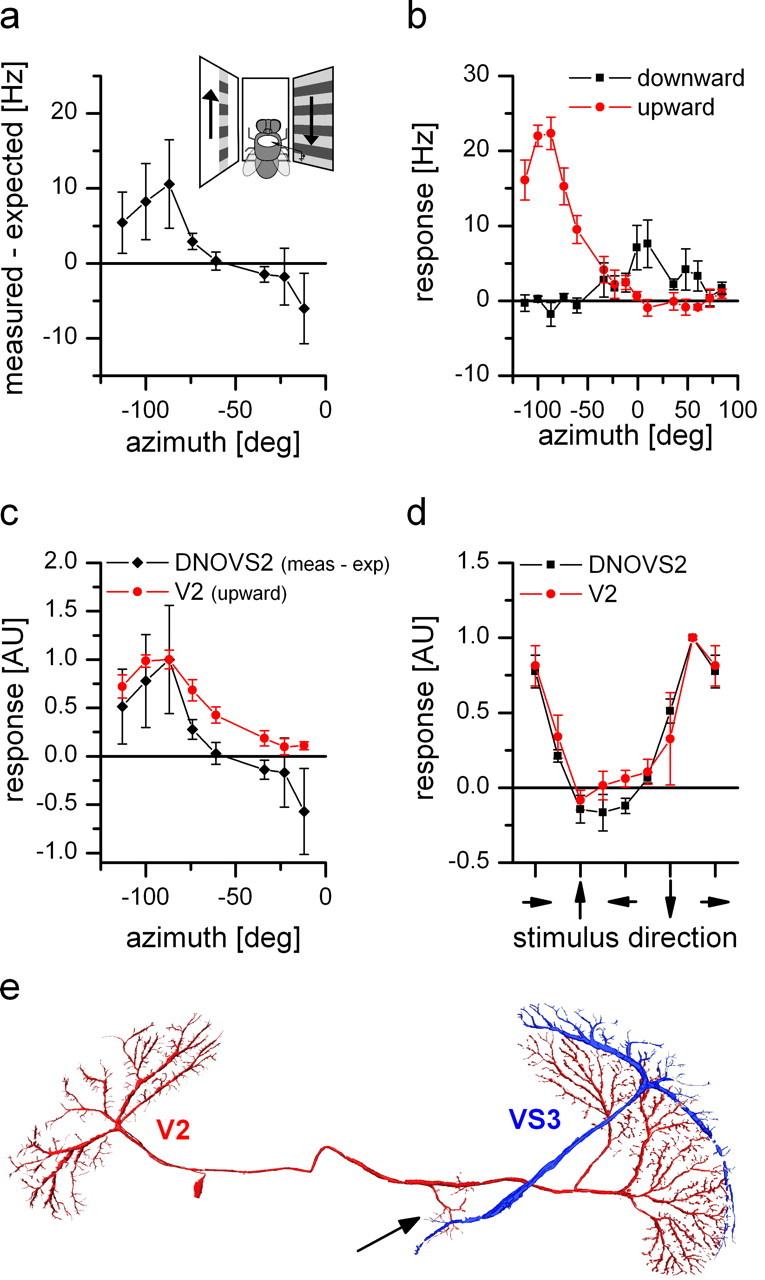
Response properties and anatomy of V2. a, Nonlinear summation of DNOVS2 as a function of the azimuth (black line). The difference between the measured response and the arithmetic sum of DNOVS2 for ipsilateral downward and contralateral upward motion is calculated for different azimuth positions. The contralateral stimulus was presented in 12° wide stripes at different position along the azimuth. At more lateral positions, the measured response of DNOVS2 is higher than the arithmetic sum, which indicates a supralinear integration. In contrast, for more frontal positions, the response of the cell is less than the arithmetic sum, indicating a sublinear integration. The highest nonlinearity was elicited at azimuth position of −87°. Data represent the mean value recorded from n = 2 flies. b, Response of V2 to vertical motion as a function of the azimuth position. The highest responses to vertical motion is elicited at lateral stimulus positions at approximately −87° in which upward motion increased the firing rate of the cell. In addition, V2 responds to motion in the frontal part with an inversed preferred direction. Data represent the mean value recorded extracellularly from n = 5 flies. Error bars represent the SEM. c, Overlay of the normalized sensitivity of V2 for upward motion (red) and the normalized nonlinearity profile of DNOVS2 (black) along the azimuth. The curves have a similar shape with a peak at the same azimuth position. AU, Arbitrary units. d, Orientation tuning of V2 (red) and DNOVS2 (black) in the frontal part of the visual field. The response normalized to the maximum response as a function of the stimulus direction is shown. The tuning curves of DNOVS2 and V2 are almost identical with a response maximum for oblique motion down to the right. Data represent the mean ± SEM of V2 (n = 4; extracellular), DNOVS2 (n = 3; 1 × intracellular + 2 × extracellular). e, Anatomy of V2. V2 and VS3 cells were filled intracellularly with the fluorescent dye Alexa 488 or Alexa 568, respectively. V2 is a heterolateral neuron projecting from one lobula plate to the other with en passant collateral to the terminal region of VS cells (arrow).
