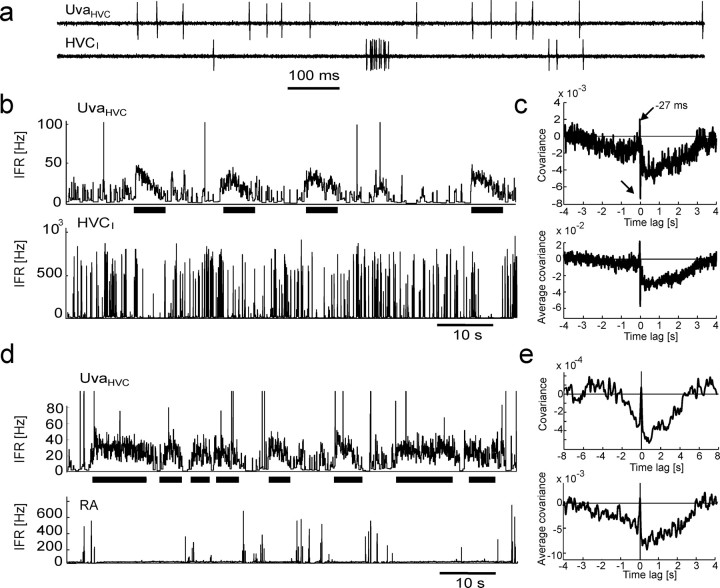
Figure 2.
UvaHVC neuron spikes are negatively correlated with spikes in HVCI neurons and bursts in RA neurons. a, Extracellular record of an UvaHVC–HVCI pair recorded during sleep. b, IFR functions of the neurons in a. Periods of high UvaHVC firing (top, thick horizontal bars) are coincident with periods of reduced HVCI bursting (bottom). UvaHVC bursts >100 Hz have been truncated for better visibility of low firing rates. c, The cross-covariance function of this neuron pair (top) and the average covariance function of n = 7 UvaHVC–HVCI pairs in three birds (bottom) both exhibit a broad dip extending up to 3 s of UvaHVC spikes and sharp positive and negative peaks close to zero time lag (arrows). To not smear over the sharp peaks, almost no smoothing was applied (4-ms-wide Gaussian). d, e, Same as b and c, but for RA instead of HVCI neurons (n = 8 UvaHVC–RA pairs). RA single spikes have been removed for the computation of covariance functions (see Materials and Methods). Smoothing was performed with a 20-ms-wide Gaussian.