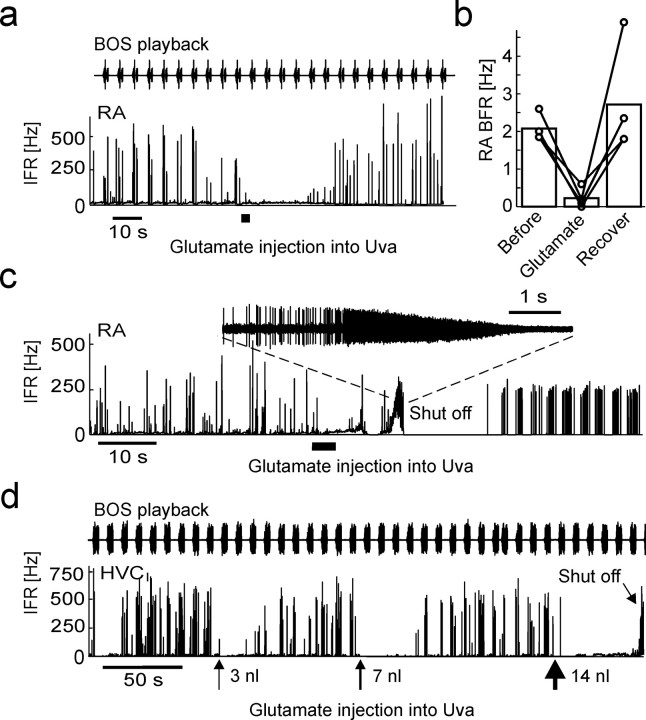
Figure 9.
Dose-dependent effects of glutamate injections into Uva. a, IFR response of an RA neuron to BOS playback during sleep. During the time interval marked by the thick horizontal line, 23 nl of 50 mm glutamate is injected into Uva, leading to a transient suppression of BOS-locked bursting. b, Bar plot summarizing the reduction in RA burst-firing rate in the 15 s interval after glutamate injections, compared with the 15 s interval before the injection. The connected circles depict data from different injections (n = 3 birds). c, Spontaneous sleep-related spiking is shut off in this RA neuron after injecting 110 nl of 100 mm glutamate into Uva. Spiking recovers within several seconds, but with visibly different statistics than before. The inset shows the shut-off event in which extracellular spike amplitudes dissapear in noise. d, Illustration of dose dependence of shut-off effect. In this HVCI neuron, BOS responses were transiently suppressed after 3 and 7 nl injections of 1 m glutamate into Uva. Approximately 1 min after a 14 nl injection, the HVCI neuron shut off (tilted arrow).