Figure 1.
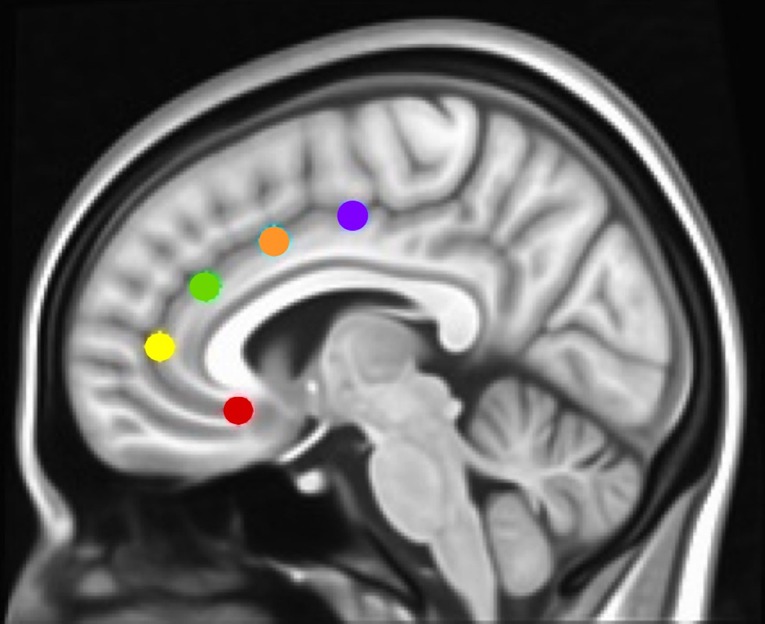
Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) sagittal view showing anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) seeds. Using the same methods as in Margulies et al. and Kelly et al. (17, 42), and our studies [Camchong et al., e.g., Refs. (27, 45, 46)], we examined the rsFC (resting-state functional connectivity) of five bilateral seed regions of interest (ROIs) located along the ACC: caudal ACC (blue; MNI coordinates: x = ±5, y = 10, z = 47), dorsal ACC (cyan; x = ±5, y = 14, z = 42), rostral ACC (green; x = ±5, y = 34, z = 28), perigenual ACC (yellow; x = ±5, y = 47, z = 11), and subgenual ACC (red; x = ±5, y = 25, z = 10). Each spherical seed covered 257 voxels in 1 × 1 × 1mm space with a radius of 3.5 mm with left and right hemispheres combined.
