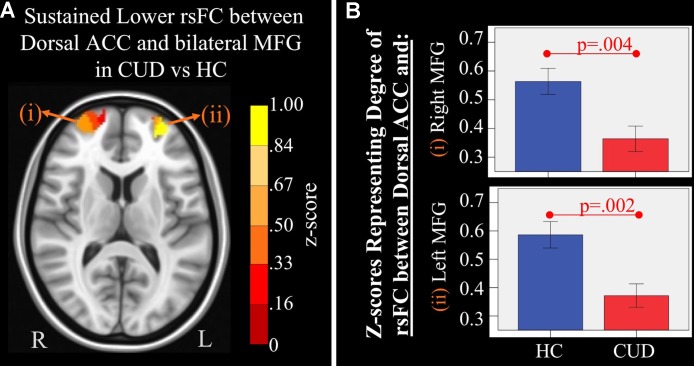
Figure 4.
Main effect of group of dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) resting-state functional connectivity (rsFC) identified by a 2 × 2 mixed-model (group × time) analysis controlling for alcohol and nicotine. (A) LEFT: Axial Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) brain slice (z = 11) illustrating clusters that showed a significant main effect of group in rsFC between the dorsal ACC seed and (i) right medial frontal gyrus (MFG; Brodmann area 10; 276 voxels) and (ii) left MFG (Brodmann area 10; 293 voxels). (B) RIGHT: Bar graphs representing mean (error bars: +/− 1 standard error) illustrating significant main effects characterized by lower rsFC between dorsal ACC and (i) right middle frontal gyrus (MFG) (F = 9.621, p = 0.004) and (ii) left MFG (F = 11.278, p = 0.002) in individuals with cannabis use disorder (CUD) than healthy controls (HC) across time.