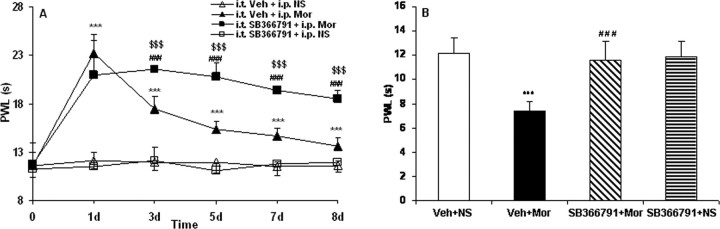
Figure 5.
Effects of intrathecal administration of the TRPV1 inhibitor SB366791 on morphine tolerance (A) and tolerance-associated thermal hyperalgesia (B) assessed by the PWL test. Although morphine consistently produced significant antinociception until day 8 (A; ***p < 0.001, Veh + Mor vs Veh + NS), the effect gradually declined during chronic exposure from day 3 to day 8, which was accompanied by thermal hyperalgesia on day 8 (B; ***p < 0.001, Veh + Mor vs Veh + NS). Rats in the morphine group pretreated with SB366791 displayed significantly longer PWLs from day 3 to day 8 (A; $$$p < 0.001 for SB366791 + Mor vs Veh + Mor, and ###p < 0.001 for SB366791 + Mor vs Veh + NS) and also had attenuated morphine-induced thermal hyperalgesia on day 8 (B; ###p < 0.001, SB366791 + Mor vs Veh + Mor). Neither Veh + NS nor SB366791 + NS treatment altered pain thresholds throughout the observation period. Two-way (A) and one-way (B) ANOVA, followed by Tukey's test were used for statistical analysis. n = 6 for each group.