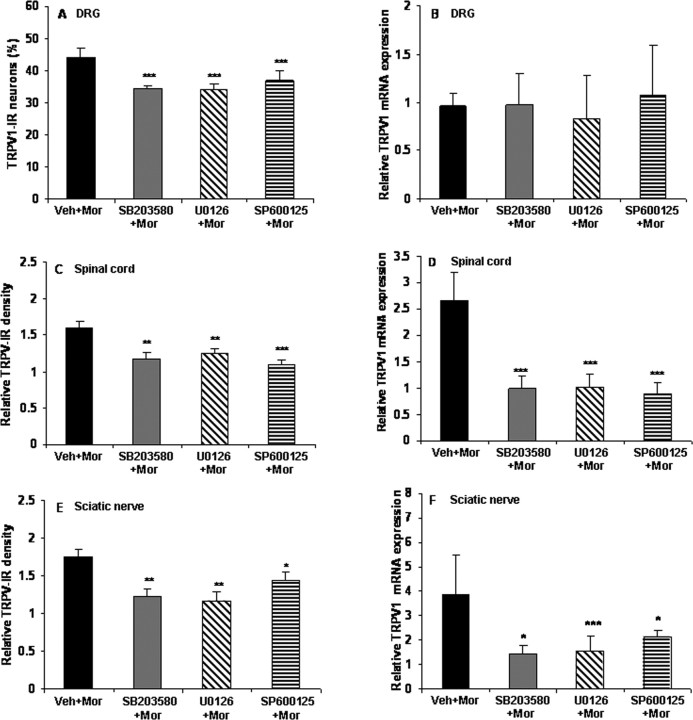
Figure 9.
Chronic morphine increases TRPV1-IR in DRG, spinal cord, and sciatic nerve and mRNA levels in spinal cord and sciatic nerve via the MAPK signaling pathway. Chronic morphine-induced increase of TRPV1-IR in DRG neurons (A) and enhanced density of TRPV-IR in the spinal superficial dorsal horn (C) and sciatic nerve (E) was reduced by pretreatment with the selective MAPK inhibitors (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 for SB203580 + Mor, U0126 + Mor, or SP600125 + Mor vs Veh + Mor). Pretreatment with the selective MAPK inhibitors did not produce significant effects on TRPV1 mRNA levels in the DRGs (B) but greatly reduced the increase of TRPV1 mRNA levels in both spinal cord and sciatic nerve (D, F; *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001 for SB203580 + Mor, U0126 + Mor, or SP600125 + Mor vs Veh + Mor) of morphine-tolerant rats. One-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's test was used for statistical analysis. n = 6 for each group.