Figure 7.
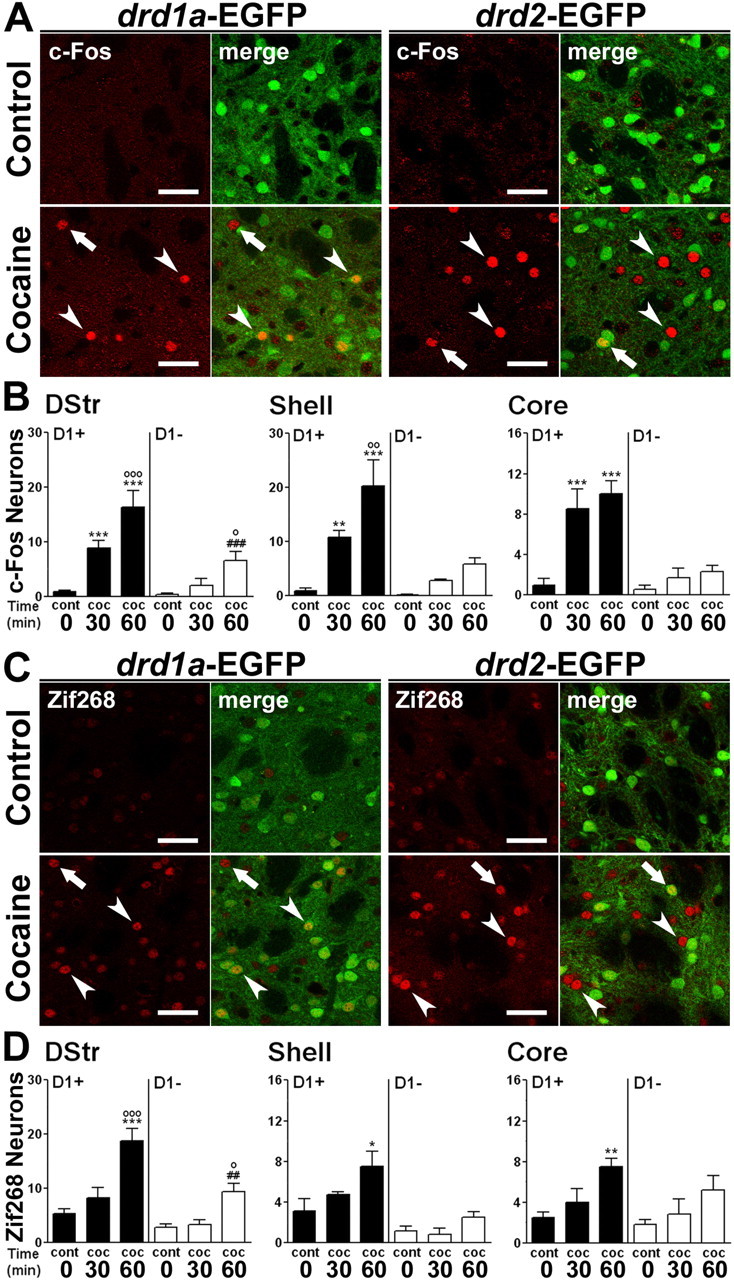
Acute cocaine exposure induces IEG expression in striatal D1R-expressing neurons and, to a lesser extent, in D2R-expressing neurons. A, C, Fluorescence of EGFP (green) and c-Fos (A) or Zif268 (C) immunoreactivity (red) in the dorsal striatum of drd1a- and drd2-EGFP mice 60 min after cocaine administration. Arrowheads indicate c-Fos (A) and Zif268 (C) expressed in D1R-expressing neurons in both strains of BAC transgenic mice. Arrows indicate c-Fos (A) and Zif268 (C) expressed in D2R-expressing neurons. Single confocal sections are shown. Scale bars, 40 μm. B, D, Quantification of c-Fos-immunoreactive (B) and Zif268-immunoreactive (D) neurons among EGFP-positive (D1+) and EGFP-negative (D1−) neurons in drd1a-EGFP mice 30 and 60 min after acute cocaine treatment in the dorsal striatum (DStr) and in the NAc shell and core. Data (means ± SEM; n = 4–8 mice per group) were analyzed using two-way ANOVA (values in supplemental Table 4, available at www.jneurosci.org as supplemental material). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, group cont 0 versus groups coc 30 and coc 60 (D1+); ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, group cont 0 versus groups coc 30 and coc 60 (D1−); ∘p < 0.05, ∘∘p < 0.01, ∘∘∘p < 0.001, group coc 30 versus coc 60 (Bonferroni test). cont 0, Control (0 min cocaine); coc 30, cocaine (30 min); coc 60, cocaine (60 min).
