Figure 8.
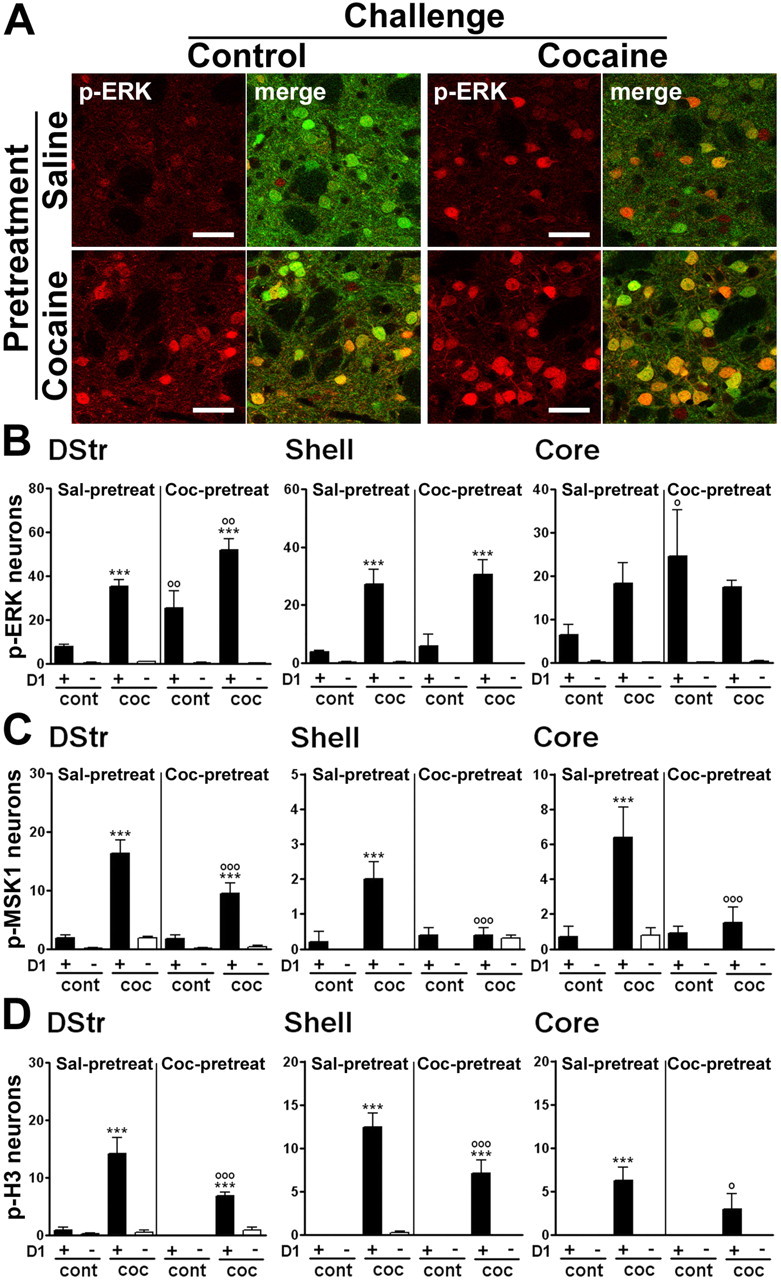
A cocaine challenge in mice previously exposed to this drug activates ERK, MSK1, and H3 phosphorylation exclusively in D1R-expressing neurons. Mice received a pretreatment with saline or cocaine and, after a 6 d withdrawal, a challenge injection of saline or cocaine (20 mg/kg). A, Fluorescence of p-ERK immunoreactivity (red) and EGFP (green) in the dorsal striatum, 15 min after a challenge injection of saline (control, left) or cocaine (right) in saline-pretreated (Sal-pretreat; top) or cocaine-pretreated (Coc-pretreat; bottom) drd1a-EGFP mice. Single confocal sections are shown. Scale bars, 40 μm. B–D, Quantification of p-ERK-immunoreactive (B), p-MSK1-immunoreactive (C), and p-H3-immunoreactive (D) neurons among EGFP-positive (D1+) or EGFP-negative (D1−) neurons in various striatal regions of drd1a-EGFP mice treated as in A. In the dorsal striatum (DStr) and NAc core of cocaine-pretreated mice, saline injection (cont) increased the number of p-ERK-positive neurons. In the dorsal striatum of cocaine-pretreated mice, cocaine injection (coc) induced more p-ERK-positive neurons than in saline-pretreated mice. Data (means ± SEM; n = 4–7 mice per group) were analyzed using three-way ANOVA (values in supplemental Table 5, available at www.jneurosci.org as supplemental material). ***p < 0.001, cont vs coc; ∘p < 0.05, ∘∘p < 0.01, ∘∘∘p < 0.001, saline-pretreated versus cocaine-pretreated (Bonferroni test). ∘∘∘p < 0.001, saline-pretreated versus cocaine-pretreated (Bonferroni test).
