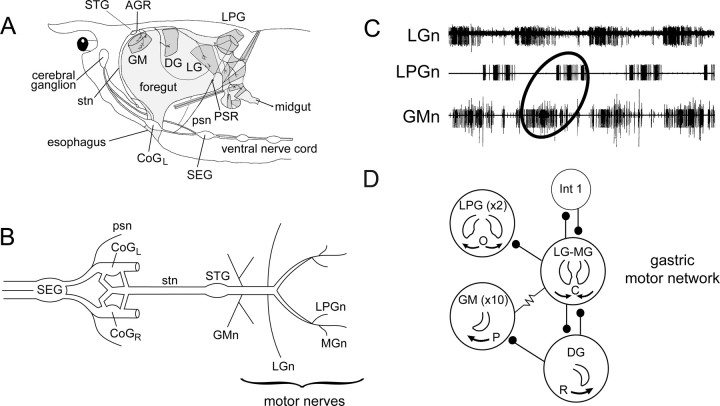
Figure 1.
The STNS and gastric mill network of the lobster Homarus gammarus. A, Lateral view showing location of the foregut, gastric mill muscles, and STNS in situ. B, Isolated STNS in vitro. The gastric mill motor circuit, including the GM, LG–MG, DG, and LPG motoneurons, is located in the STG, from which their axons project caudally in separate bilateral nerve branches. The STG is connected to the two CoGs and the SEG via the single stn. C, Typical gastric mill output pattern recorded extracellularly from indicated gastric motor nerves (n) in an isolated STNS. GM motoneurons fire in antiphase with LPG motoneurons and in phase with the LG motoneuron. D, Synaptic connectivity of the gastric mill network. Stick and ball symbols, Chemical inhibitory synapses; resistor symbol, electrical coupling. Numbers of neurons of each type are indicated in parentheses, when involving more than a single neuron. Neurons of each functional group are electrically coupled, including the LG–MG neurons. Gastric teeth movements driven by each neuron type is also indicated. GM and DG motoneurons are responsible for protraction (P) and retraction (R) of the medial tooth, whereas LPG and LG–MG neurons drive opening (O) and closing (C) of the lateral teeth. The gastric mill network also contains a single interneuron, Int 1. CoGL, Left CoG. CoGR, Right CoG.