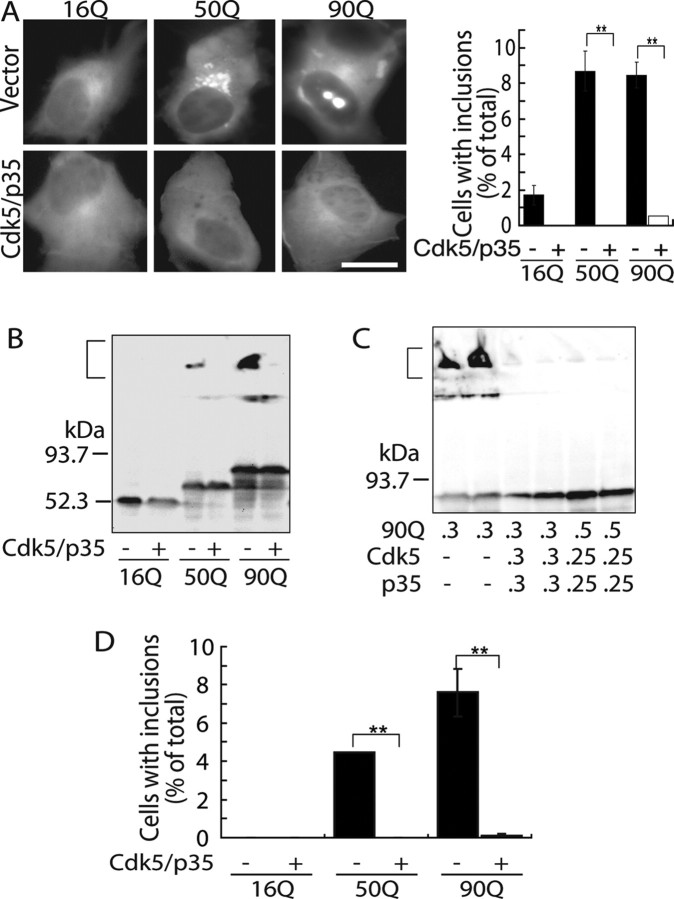
Figure 1.
Suppression of the formation of mhtt inclusions by Cdk5/p35. A, Fluorescence microscopic images of tNhtt-16Q, 50Q, or 90Q-EGFP expressed alone (top panels) or coexpressed with Cdk5/p35 (bottom panels) in COS-7 cells (left panels). Cells were analyzed for inclusion formation 24 h after transfection. Scale bar, 10 μm. Quantification of cells containing EGFP inclusions is shown in the right panel (mean ± SEM; **p < 0.001). B, Detection of SDS-insoluble aggregates in COS-7 cells expressing 50Q or 90Q but not 16Q by anti-GFP immunoblotting. A bracket indicates aggregates in the stacking gel. C, Inhibition of tNhtt-90Q-EGFP inclusion formation by Cdk5/p35 when cotransfected in different plasmid ratios. The amount of plasmid DNA (in micrograms) used is indicated below the blot. A bracket indicates SDS-insoluble aggregates. D, Inclusion formation of tNhtt-16Q, 50Q, 90Q-EGFP and suppression by Cdk5/p35 in Neuro2a cells. The number of cells containing EGFP-aggregates was counted and expressed as the percentage ratio to total EGFP-positive cells transfected in the presence (+) or absence (−) of Cdk5/p35 (mean ± SEM; **p < 0.001).