Figure 1.
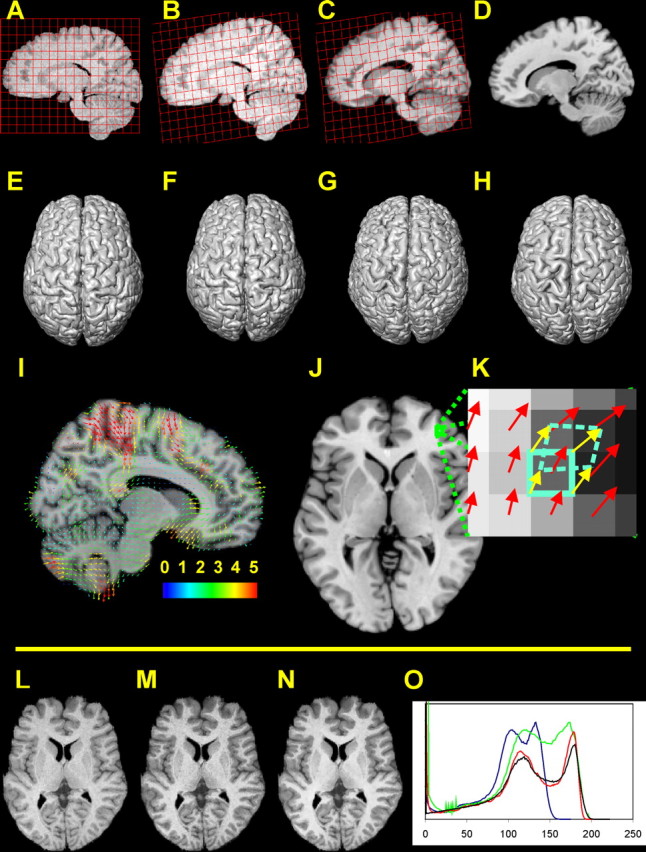
A–H, Registration of a brain image (sagittal sections and dorsal view of a 3D reconstruction); a regular grid is overlaid on the sagittal sections of the source MR image and is transformed in the same way as the brain image. A, E, Segmented brain image before registration. B, F, Result of the affine transformation. C, G, Result of the nonlinear registration. D, H, Reference image. I, Deformation field. Only a subset of the deformation vectors is presented (for the sake of visualization). The starting point of each vector is related to the reference image. The endpoint of each vector marks the corresponding point in the individual source image (after the affine transformation). The colors of the vectors indicate their length in millimeters. J, K, Calculation of local volume ratios on the voxel scale (in two dimensions). J, Horizontal section of the reference brain. K, Magnified part of the section in J. The starting point of a deformation vector (red arrows) is located in the center of each voxel of the reference image. Consider the voxel within the cyan frame (solid line): the deformation vectors of the corner points of this voxel (yellow arrows) are calculated by interpolating the original deformation vectors. The endpoints of the interpolated deformation vectors define the positions of the corner points within the source image (after the affine transformation). Thus the volume of the distorted voxel (dashed cyan line) within the space of the source image can be calculated. To calculate 3D volumes, this procedure is applied to the eight corner points of a cubical voxel. L–O, Matching of intensity values and edge-preserving filtering. L, MR image with original intensity values. M, MR image after having matched its histogram with the histogram of the reference image. N, Result of applying the edge-preserving SUSAN filter (Smith et al., 2001). O, Intensity histograms of the MR images in L–N and of the reference image. Blue, Original histogram (L); green, matched histogram (M); red, histogram of the filtered image (N); black, histogram of the reference image. A transformation of the voxel values regardless of the voxel positions leads from L to M. The gray and white matter peaks in the histograms of M and the reference image (green and black line) match quite well (O). However, the contrast is low. Therefore, the edge-preserving filtering is applied, creating an image with visibly enhanced contrast-to-noise ratio (N). It should be noted that the intensity values in the SUSAN-filtered and the reference image are more densely distributed than in the original and histogram-matched images, leading to generally lower frequencies in the histograms of the former two images. Thus the deepening of the valley between the GM and WM peak in the histogram of the SUSAN-filtered image is in part attributable to the stretching and redistribution of the intensity values in-between these peaks.
