Figure 12.
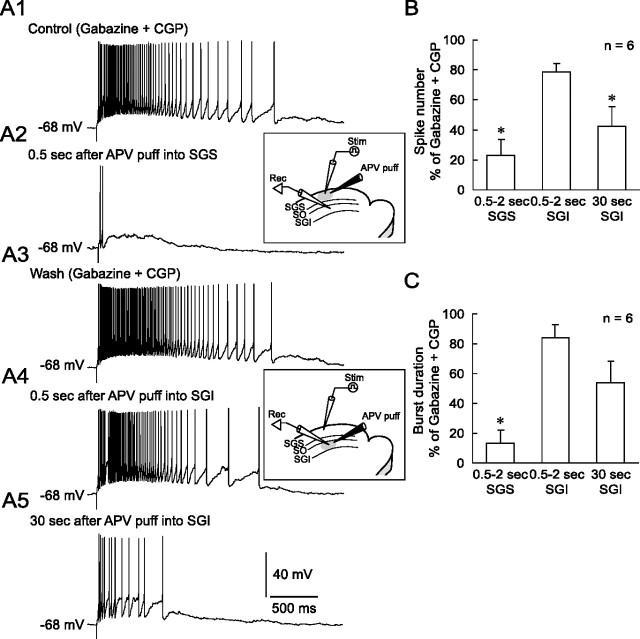
NMDAR-dependent bursts in the SGS are necessary for long-lasting burst generation in the SGI. A1, In the presence of gabazine and CGP, SGS stimulation evoked long-lasting bursts in an SGI non-GABAergic neuron. A2, The stimulation induced only two action potentials and slow depolarization 0.5 s after puff application of APV locally to the SGS. Inset, Schematic showing the arrangement of recording and stimulating electrodes and puff pipette for application of APV (5 mm) into the SGS. A3, The effect of APV was reversible upon washout. A4, In the same SGI neuron, puff application of APV into the SGI 0.5 s before stimulation slightly inhibited the bursts. Inset, Schematic showing the arrangement of recording and stimulating electrodes and puff pipette for application of APV (5 mm) into the SGI. A5, The burst was further inhibited 30 s after APV application. B, A summary graph showing the effects of local APV application into the SGS or SGI on the number of spikes within a burst. The puff application of APV into the SGS significantly reduced the spike number. C, A summary graph showing the effect of local APV application into the SGS or SGI on the burst duration. Again, the puff application of APV into the SGS significantly decreased the burst duration. *p < 0.05, compared with control.