Figure 8.
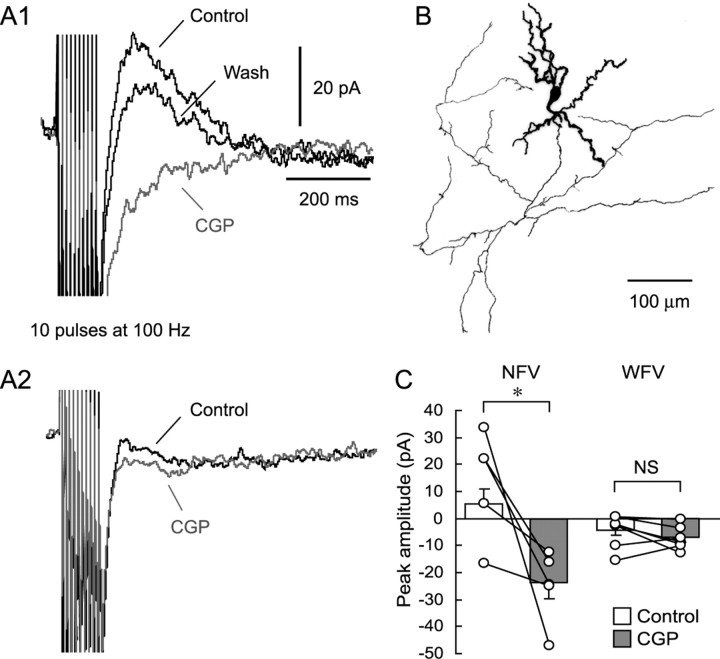
Local repetitive stimulation elicited CGP-sensitive currents in NFV but not WFV cells. A1, Voltage-clamp recordings obtained from an NFV cell show that repetitive local stimulation in the SGS evoked outward currents (black trace, Control), which were abolished by CGP application (gray trace, CGP). Recordings were performed in the presence of CNQX (10 μm), APV (50 μm), and gabazine (10 μm) at a holding membrane potential of −60 mV. Note that ionotropic glutamate receptor antagonist-insensitive inward currents were unmasked by CGP application. The effect of CGP was recovered after washout (black trace, Wash). A2, SGS repetitive stimulation did not evoke a clear CGP-sensitive current in a WFV cell. Membrane potential was held at −60 mV. B, Morphology of the biocytin-filled NFV cell, from which the responses shown in A1 were obtained. Soma and dendrites are drawn as thick lines and axons as thin lines. C, A summary graph showing the effect of CGP on the repetitive stimulation-induced currents. Open circles represent individual neurons. Bar graphs indicate average current amplitude of each condition. *p < 0.05. NS, Not significant.