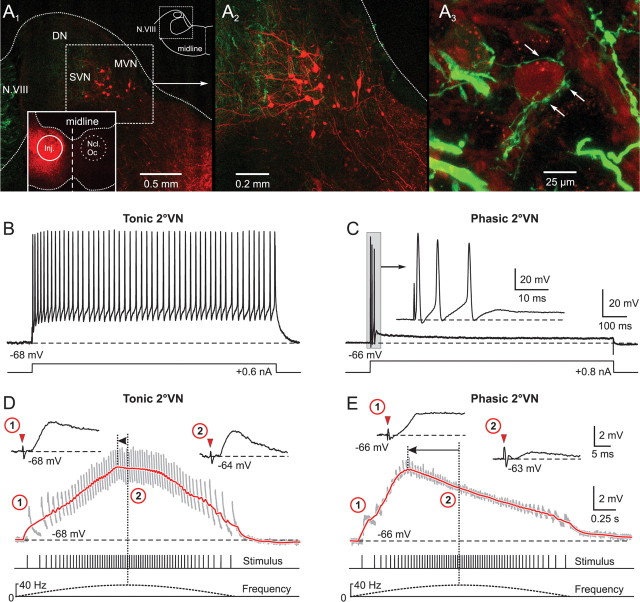
Figure 2.
Synaptic compound responses evoked by pulse-train stimulation of semicircular canal nerves in identified central vestibular neurons. A1, The location of retrogradely labeled vestibulo-ocular neurons in the superior vestibular nucleus (SVN) and MVN after injection of Alexa Fluor 546 dextran (red) into the ipsilateral oculomotor nucleus (Ncl Oc; inset) help determine the area for the recordings in the isolated frog brain. A2, Higher magnification of labeled SVN and MVN vestibulo-ocular neurons located in the outlined area in A1. A3, AC afferent fibers, labeled in green from the periphery with Alexa Fluor 488 dextran, contact the soma (arrows) of a neuron in the SVN. B, C, A continuous discharge (B) and a short burst of three spikes (C) evoked by intracellular injection of long positive current steps (bottom traces) characterized tonic (B) and phasic 2°VNs (C), respectively. The inset in C shows the short initial burst (gray area) of the phasic 2°VN at an extended time scale. D, E, Compound responses formed by temporal summation of individual EPSPs (gray traces) after pulse-train stimulation of the AC nerve with a peak frequency of 40 Hz in the same tonic (D) and phasic 2°VN (E) as shown in B and C, respectively. The bottom traces indicate pulse train and stimulus frequency. Insets in D and E show EPSPs evoked by the first single pulse of the train (1) and by the single pulse at peak frequency (2) at an extended time scale; horizontal dashed lines in B–E indicate the membrane potential (−68 mV in B, D; −66 mV in C, E). Red arrowheads in insets in D and E indicate the single pulses. Red traces in D and E are smoothed fits of the compound responses; horizontal arrows indicate the advance of the compound response peak with respect to stimulus peak frequency (vertical dotted lines). Records in B and C are single sweeps, and in D and E are the average of 12 responses. Calibrations in C and E apply to B and D, respectively. DN, Dorsal auditory nucleus.