Figure 2.
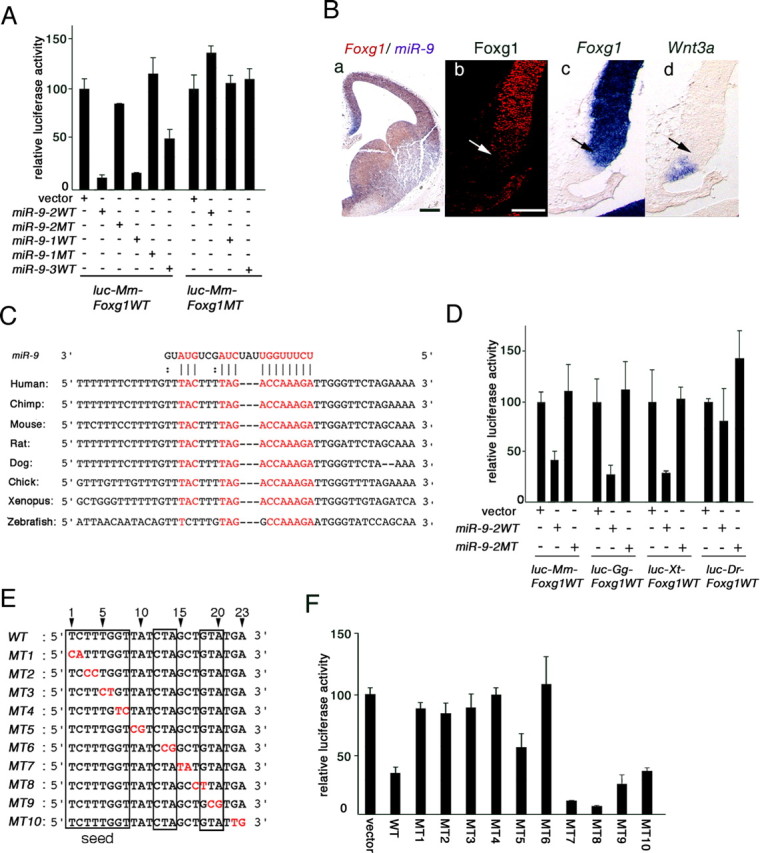
miR-9 targets Foxg1 3′UTR. A, Essential roles of seed sequence and target sequence in suppression of Foxg1 3′UTR by miR-9. Effects of WT or MT miR-9-1, miR-9-2, or miR-9-3 on Luciferase expression from luciferase reporters conjugated with WT or MT Foxg1 3′UTR are shown (for the details, see supplemental material, available at www.jneurosci.org). In all the assays, the luciferase expression was nearly the same at the mRNA level. B, Foxg1 spatial expression pattern in the medial pallium. Ba, miR-9 (purple) and Foxg1 (brown) mRNA expression in E12.0 telencephalon; Bb–Bd, Foxg1 protein, Foxg1 mRNA, and Wnt3a mRNA expression boundaries. Arrows in Bb–Bd indicate the limits of cortical hem marked by Wnt3a (Bd). Scale bars: Ba, 200 μm; Bb–Bd, 100 μm. C, Conservation of miR-9 target sequences in vertebrate Foxg1 3′UTRs. D, Luciferase assay of miR-9 suppression of mouse (Mm), chick (Gg), Xenopus (Xt), and zebrafish (Dr) Foxg1 3′UTRs. E, Two-base mutations in miR-9 as indicated in red (MT1–10). Sequences assumed to make base pairing in the wild-type miR-9 with Foxg1 target sequence are boxed. F, Luciferase assay of the Foxg1-suppressing activities of miR-9-2 mutated as shown in E.
