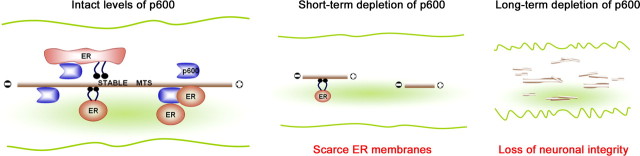
Figure 6.
Model depicting the interaction between p600, MTs, and ER. p600 associates with stable MTs and binds to ER. p600 may couple MT stability and dynamics to ER transport, tubule extension, and morphogenesis. A short-term loss of p600 destabilizes MT, reduces anterograde ER transport, and causes retraction of existing ER in neuronal processes, including the leading process. Over time, the disruption of the MTs–ER interface can alter the integrity of these processes, thereby impeding neurite outgrowth and neuronal migration during development. In this model, ER membranes are transported via “sliding mechanism” (with molecular motors) and “MT movement mechanism” (ER membranes attached to MTs).