Figure 2.
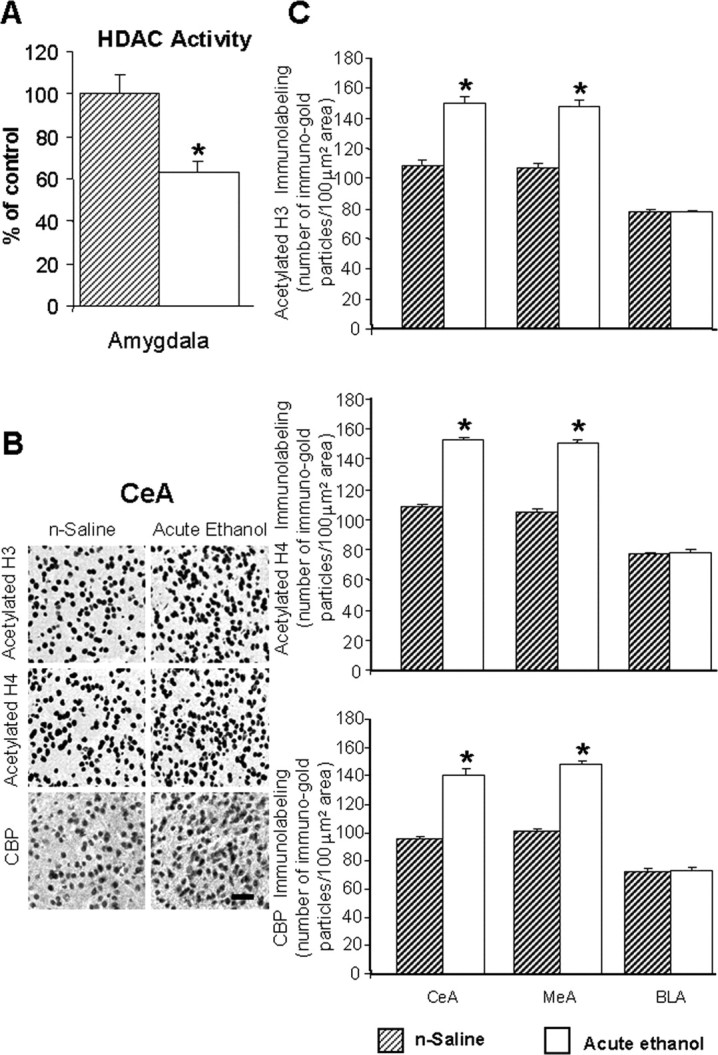
A, Acute ethanol exposure inhibited HDAC activity in the amygdala of rats [injected with ethanol (1 h after 1 g/kg, i.p.) or n-saline]. The HDAC activity was determined in the cell lysates of amygdala by measuring the deacetylation of acetylated lysine side chains. The values are the mean ± SEM of seven rats per group. *Significantly different from n-saline-treated rats (p < 0.01; Student's t test). B, Low-magnification photomicrographs of acetylated histones H3 (Lys 9) and H4 (Lys 8) and CBP gold-immunolabeling (protein levels) in central amygdaloid (CeA) structures of n-saline or acute-ethanol-treated rats. Scale bar, 40 μm. C, Effect of acute ethanol treatment on protein levels of acetylated H3 and H4, and of CBP in various amygdaloid (CeA, MeA, and BLA) structures of rats. Values are the mean ± SEM of seven to nine rats per group. *Significantly different from the n-saline-treated rats (p < 0.001; Student's t test).
