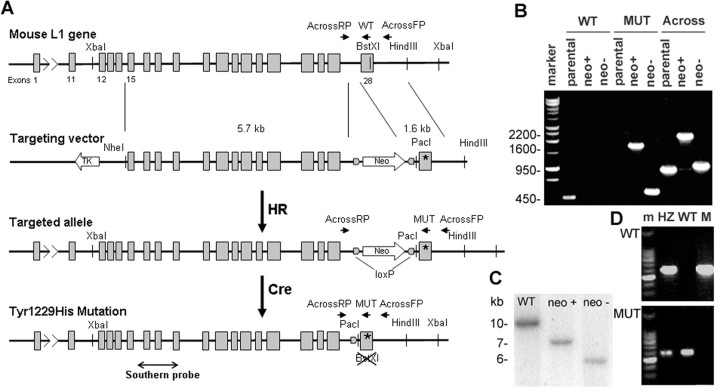
Figure 1.
Generation of the L1(Y1229H) knock-in mouse. A, Schematic representation of the genetic modification at the L1 locus: wild-type exon 28 was replaced by a modified exon 28 in which the codon corresponding to 1229Tyr was changed to encode His by homologous recombination (HR) in ES cells; the neomycin-resistance gene introduced at the same time in intron 27, was subsequently removed by cre-mediated recombination in ES cells (Cre). B, PCR analysis of ES clones (parental ES cells, neomycin-positive clone after HR, neomycin-negative clone after cre recombination; marker, 1 kb DNA ladder). Lanes 1–3, PCR for the wild-type allele, using the WT and AcrossL1RP primers. Lanes 4–6, PCR for the mutant allele, using the MUT and AcrossL1RP primers. Lanes 7–9, PCR covering the region modified by recombination, using the AcrossL1 FP and RP primers. C, Southern blot screening of recombined neomycin-positive clones and neomycin-negative clones after cutting with XbaI and PacI (site introduced through recombination), using a probe corresponding to exons 16–19. D, Mouse genotyping by PCR using allele specific primers: top row, MUT and AcrossL1RP; bottom row, WT and AcrossL1RP; m, marker (100 bp DNA ladder); HZ, heterozygote female; WT, wild-type male; M, hemizygous L1YH.