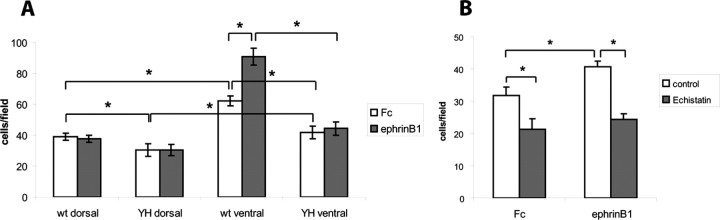
Figure 7.
L1/ankyrin interaction promotes ephrinB1-stimulated, integrin-mediated retinal cell adhesion. A, Retinal cell adhesion to fibronectin was quantified by determining the mean number of cells per field from three or more independent assays. Adhesion of WT ventral retinal cells to fibronectin was greater than WT dorsal retinal cells, and was stimulated by ephrinB1-Fc. Adhesion of L1(Y1229H) ventral retinal cells was lower than WT ventral cells and was not stimulated by ephrinB1-Fc. Total cell numbers were as follows: WT ventral retina, n = 100; WT dorsal retina, n = 80; LIYH ventral retina, n = 100; LIYH dorsal retina, n = 60. *p < 0.05, statistical significance was analyzed using the two-tailed t test. B, Echistatin peptide (5 μg/ml), an inhibitor of RGD-binding integrins, decreased adhesion of WT ventral retinal cells to fibronectin-coated dishes treated with preclustered ephrinB1-Fc fusion protein (1 μg/ml) or Fc control protein. A representative experiment (from a total of 3 experiments) is shown with n = 20 cells per condition. Statistical significance was analyzed using the two-tailed t test, *p < 0.05.