Figure 6.
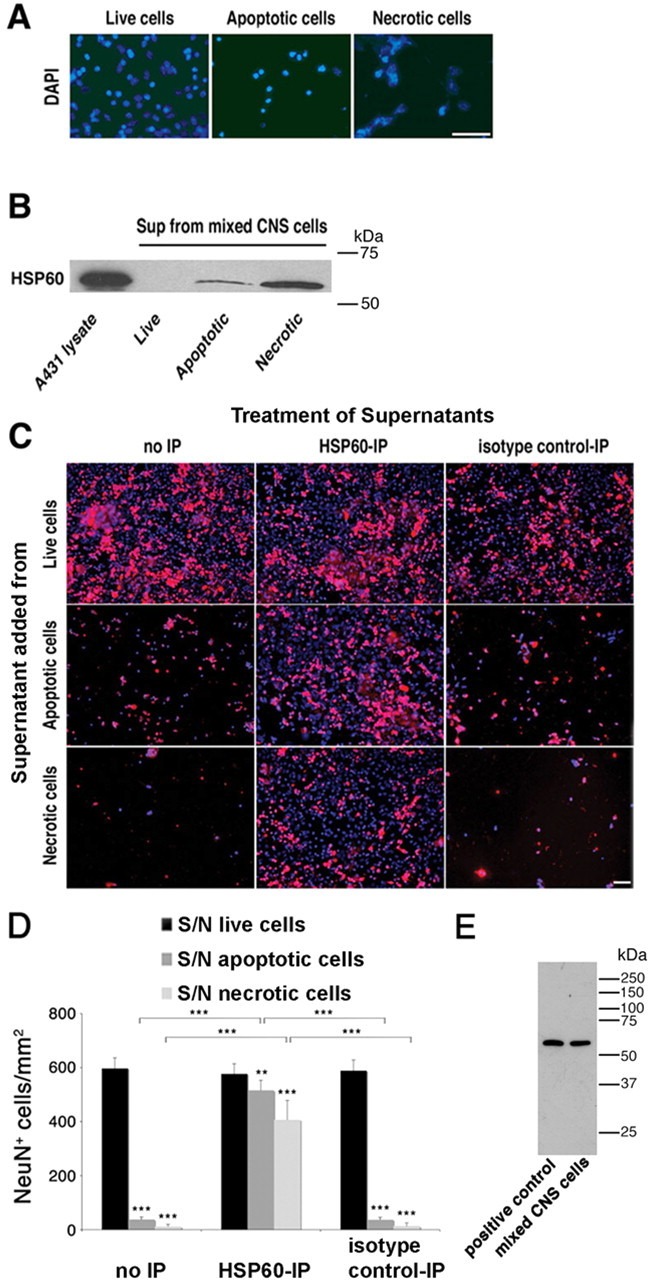
HSP60 is released by apoptotic and necrotic CNS cells and causes neuronal injury. Mixed CNS cultures derived from wild-type mice were forced to undergo apoptosis or necrosis. A, Untreated and drug-treated cells were stained with DAPI. B, Culture supernatants (Sup) of treated cells were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and subsequent immunoblotting with an HSP60 antibody. Cell lysate derived from A431 cells served as a positive control. C, Culture supernatants of treated cells were immunoprecipitated with an HSP60 antibody or normal mouse IgG. Neuronal-enriched mixed CNS cultures derived from wild-type mice were treated with either plain or immunoprecipitated (with an antibody against HSP60 or with normal mouse IgG) culture supernatants of live, apoptotic, and necrotic cells. Cells were then immunostained with NeuN to mark neurons and with DAPI. D, Quantitation of NeuN-positive neurons in CNS cultures treated with supernatants (S/N) from live, apoptotic, or necrotic CNS cells with or without immunoprecipitation (IP) against HSP60. Six high-power fields per coverslip were analyzed. For each condition, experiments were performed in triplicates. The data shown are representative of three individual experiments. The results are presented as mean ± SD (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; Student's t test) for the comparison of S/N from apoptotic or necrotic cells versus S/N from live cells and for the comparison of S/N treated with anti-HSP60 antibody versus isotype control antibody or no treatment. E, Immunoblot of wild-type mouse-derived mixed CNS cells and heat-shocked HeLa cells (positive control) probed with the SPA-807 antibody. Scale bars, 50 μm.
