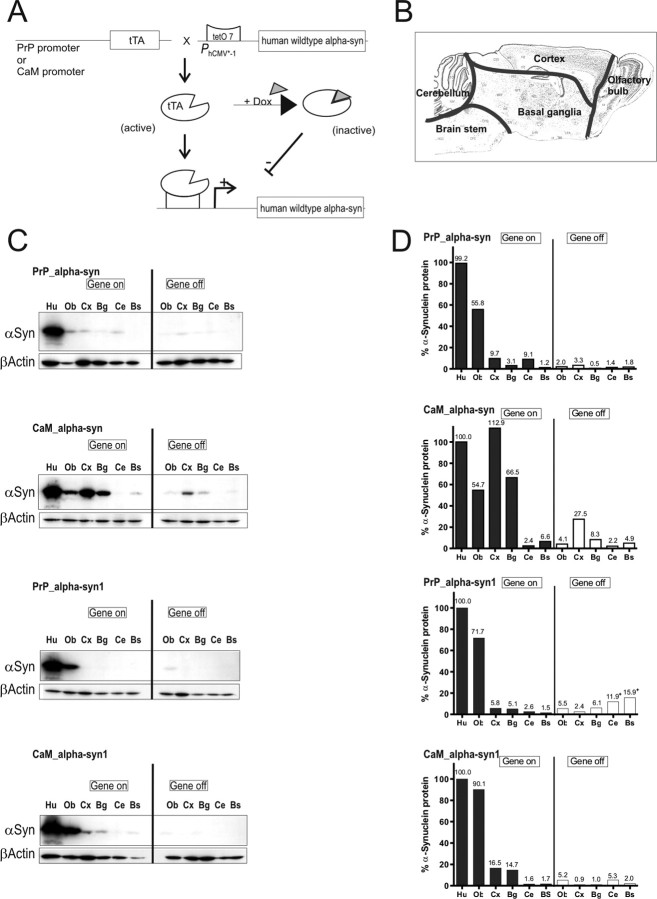
Figure 1.
Conditional mouse design and expression pattern of human α-syn in brains of tg mice. A, tTA expression was either driven by the PrP or the CaM promoter. In its active form, tTA binds to the tetO7 sequence of the minimal promoter and initiates expression of the downstream localized human α-syn gene. Expression can be inhibited by the presence of dox, because it binds to tTA, making it inactive. B, Subregional brain dissection for Western blot analysis. The reconstructed atlas template is according to the stereotaxic atlas (Paxinos and Franklin, 2001). C, Western blot analyses (20 μg per lane) of human α-syn in dissected tg mouse brains using the 15G7-α-syn antibody and β-actin as internal loading control. After administration of dox for 3 weeks (gene off), reduced protein levels in adult double-tg mice of each line were observed. Human brain was used as positive control. D, Band intensities were quantified using ImageQuant software and normalized to the β-actin staining in the same line to correct for variations in loading. After normalization, the amount of human α-syn was calculated in percentage relative to expression intensity of the human brain signal. +, Unspecific background staining of membrane. Ob, Olfactory bulb; Cx, cortex; Bg, basal ganglia; Ce, cerebellum; Bs, brainstem; Hu, human brain.