Figure 2.
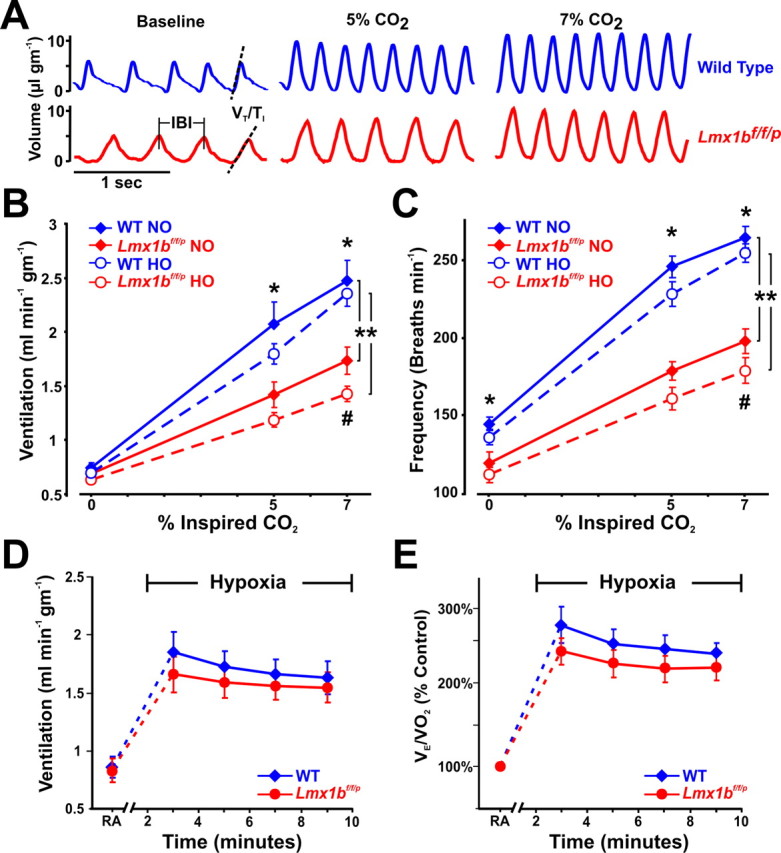
Lmx1bf/f/p mice have decreased ventilatory drive and their hypercapnic ventilatory response is severely blunted. A, Plethysmography recordings from WT (blue) and Lmx1bf/f/p (red) mice at rest, and while breathing 5% and 7% CO2 in normoxia (21% O2). Dashed lines highlight decreased slope of the inspiratory phase (ventilatory drive), and vertical lines mark the IBI. B, C, Ventilation (B) and breathing frequency (C) during hypercapnia under normoxic (NO) and hyperoxic (HO; 50% O2) conditions (n = 10 WT NO, 8 Lmx1bf/f/p NO, 11 WT HO, 8 Lmx1bf/f/p HO). D, E, Ventilation (D) and convection requirement (E; VE/VO2; expressed as a percentage of control) during exposure to room air (RA) and hypoxia (n = 8 WT, 8 Lmx1bf/f/p). For two-way ANOVA (genotype and condition as factors), **p < 0.05. For unpaired t test, *p < 0.05 (WT versus Lmx1bf/f/p) for both normoxia and hyperoxia. For paired t test, #p < 0.05 for normoxia versus hyperoxia in Lmx1bf/f/p. Data are mean ± SEM.
