Figure 8.
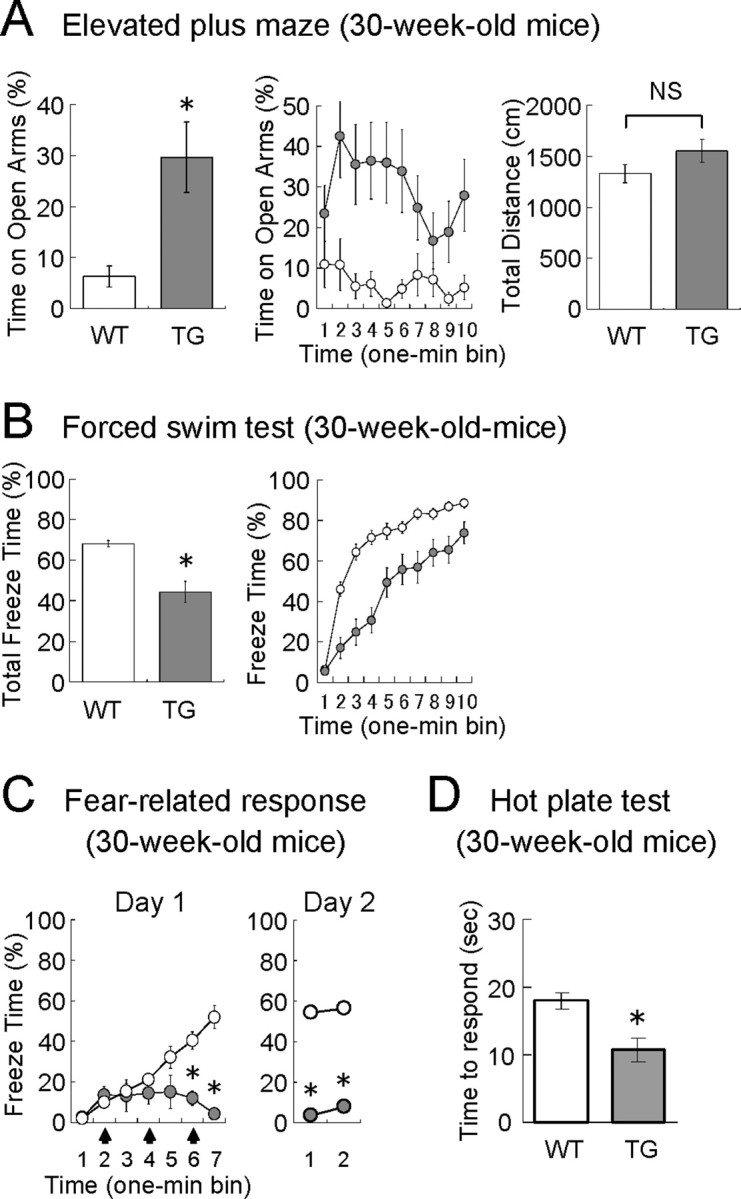
Affective behaviors in older VEGF120-TG mice. The behavioral tests were performed in 30-week-old male mice (white, WT mice; gray, TG mice). The characteristic behavioral phenotypes of TG mice were maintained at 30 weeks of age under a minimal level of neurogenesis. A, Elevated plus maze. Time on the open arms (in percentage), time on the open arms per 1 min bin (in percentage), and total distance (in centimeters) during the 10 min test period are shown. n = 20 and 15 for 30-week-old WT and TG mice. *p < 0.01, Mann–Whitney U test; p = 0.12 [nonsignificant (NS)], unpaired Student's t test. Data are as follows: time on open arms: WT mice, 6.3 ± 2.1%; TG mice, 29.6 ± 6.9%; total distance; WT mice, 1326 ± 88 cm; TG mice, 1548 ± 112 cm. B, Porsolt forced swim test. Total freeze time (in percentage) and freeze time per 1 min bin (in percentage) during the 10 min test period are shown. n = 20 and 18 for 30-week-old WT and TG mice. *p < 0.001, Mann–Whitney U test. Data are as follows: total freeze time: WT mice, 68.1 ± 1.6%; TG mice, 44.3 ± 5.3%. C, Fear conditioning. Freeze time per 1 min bin (in percentage) is shown for day 1 (conditioning) and day 2 (context-induced fear). n = 20 and 14 for 30-week-old WT and TG mice. *p < 0.01 for bins 6–7 on day 1 and bins 1–2 on day 2 (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey–Kramer's post hoc test). Data on day 1 in WT and TG mice are as follows: bin 1, 2.3 ± 1.0 and 2.7 ± 1.8%; bin 2, 10.0 ± 1.7 and 13.7 ± 4.0%; bin 3, 15.5 ± 3.8 and 13.3 ± 7.6%; bin 4, 21.2 ± 2.7 and 14.7 ± 5.3%; bin 5, 32.2 ± 5.2 and 15.2 ± 7.9%; bin 6, 40.6 ± 4.3 and 12.1 ± 3.5%; bin 7, 52.1 ± 5.5 and 4.3 ± 2.2%. Data were nonsignificant between bin 7 on day1 and bin 1 on day 2 in both genotypes (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey–Kramer's post hoc test). Data on day 2 in WT and TG mice are as follows: bin 1, 54.3 ± 4.1 and 3.8 ± 1.4%; bin 2, 56.2 ± 5.1 and 7.6 ± 2.9%. D, Hot plate test. Thirty-week-old male mice were placed on a hot plate maintained at 55°C, and the latencies (in seconds) of thermal nociception (hindpaw lick or hindpaw shake/flutter) were measured. The result indicates that TG mice are not insensitive to nociceptive stimuli. n = 20 and 14 for 30-week-old WT and TG mice. *p < 0.01, unpaired Student's t test. Data are as follows: latencies: WT mice, 18.1 ± 1.21 s; TG mice, 10.7 ± 1.78 s.
