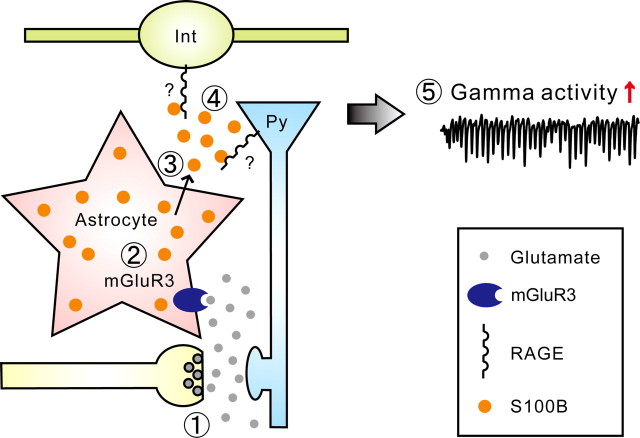
Figure 8.
Schematic representation of the proposed S100B signaling. The basal level of extracellular S100B is low in the hippocampus. The neural activity is increased upon administration of KA which increases the release of glutamate from presynaptic terminals (1) by action potentials mediated calcium influx and direct activation of kainate receptors. The excess amount of synaptically released glutamate activates astrocytic mGluR3 (2). As a result, S100B is released from the astrocyte to the extracellular space (3) by a mechanism independent of Cx43 hemichannels. The extracellular S100B binds to RAGE (4) which in turn enhances the gamma oscillation amplitude (5). The localization of RAGE remains to be determined. Py, Pyramidal cell; Int, interneuron.