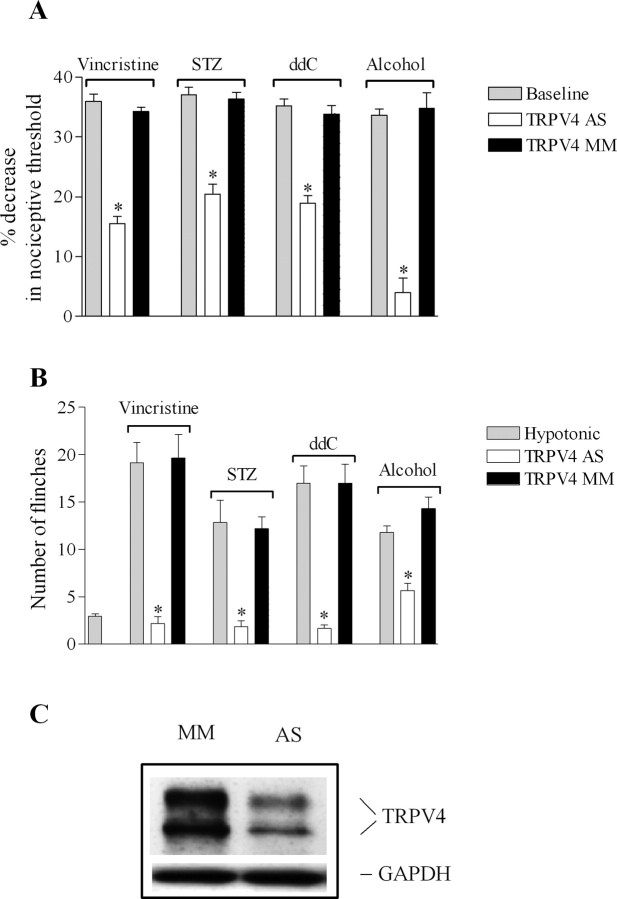
Figure 1.
Contribution of TRPV4 to the hypersensitivity for mechanical and hypotonic stimuli in diverse models of painful peripheral neuropathy. A, Rats treated with vincristine, STZ, ddC, or alcohol showed a decrease in their mechanical nociceptive thresholds (gray bars). Spinal intrathecal treatment with TRPV4 antisense (TRPV4 AS, white bars), compared with mismatch oligodeoxynucleotides (TRPV4 MM, black bars), reversed the mechanical hyperalgesia in alcohol-fed rats and reduced it by 53% in vincristine- and 44% in STZ- and ddC-treated rats, respectively. B, Injection of 10 μl of hypotonic solution induced a significantly higher number of flinches in vincristine-, STZ-, ddC-, and alcohol-treated compared with control rats. TRPV4 antisense, compared with mismatch ODN, reduced the increase in the number of flinches induced by hypotonicity by 89% in vincristine-treated (2.2 ± 1.7 for antisense- vs 19.6 ± 2.4 for mismatch-treated rats; n = 6 for each ODN group; p < 0.0001, unpaired Student's t test), 83% in STZ-treated rats (1.8 ± 0.6 for antisense- vs 12.1 ± 1.2 for mismatch-treated rats; n = 6 for each ODN group; p < 0.0001, unpaired Student's t test), 88% in ddC-treated (1.7 ± 0.3 for antisense- vs 17 ± 2 for mismatch-treated; n = 6 for each ODN group; p < 0.0001, unpaired Student's t test), and 52% in alcohol-fed rats (5.6 ± 0.7 for antisense- vs 14.3 ± 1.2 for mismatch-treated; n = 6 for each ODN group; p < 0.0001, unpaired Student's t test). C, There was a significant decrease in the level of TRPV4 protein expression in saphenous nerve from alcoholic rats treated with antisense compared with mismatch ODN-treated rats (38 ± 8%; n = 6 for each ODN group; p < 0.05, unpaired Student's t test). The amount of protein loaded in each lane was normalized by probing the membrane with an anti-GAPDH antibody. *p < 0.05.