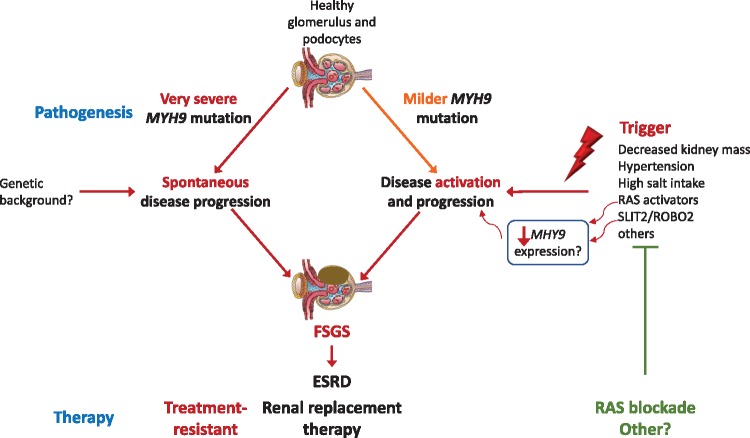
FIGURE 2.
Pathogenic working hypothesis with therapeutic implications: two pathways to MYH9-related ESRD. Hypothesis based on the high heterogeneity of kidney disease within families with the same mutation, the clinical evidence of rapidly progressive disease at very different age ranges (from childhood to adulthood to the elderly) suggestive of the existence of triggers and preclinical evidence supporting the existence of triggers such as angiotensin II hyperactivity, together with evidence that a diabetic milieu, angiotensin II or other stressors, decrease MYH9 expression. The direct therapeutic implication is that identification and treatment of triggers may slow disease progression as suggested by certain patients on RAS blockade.