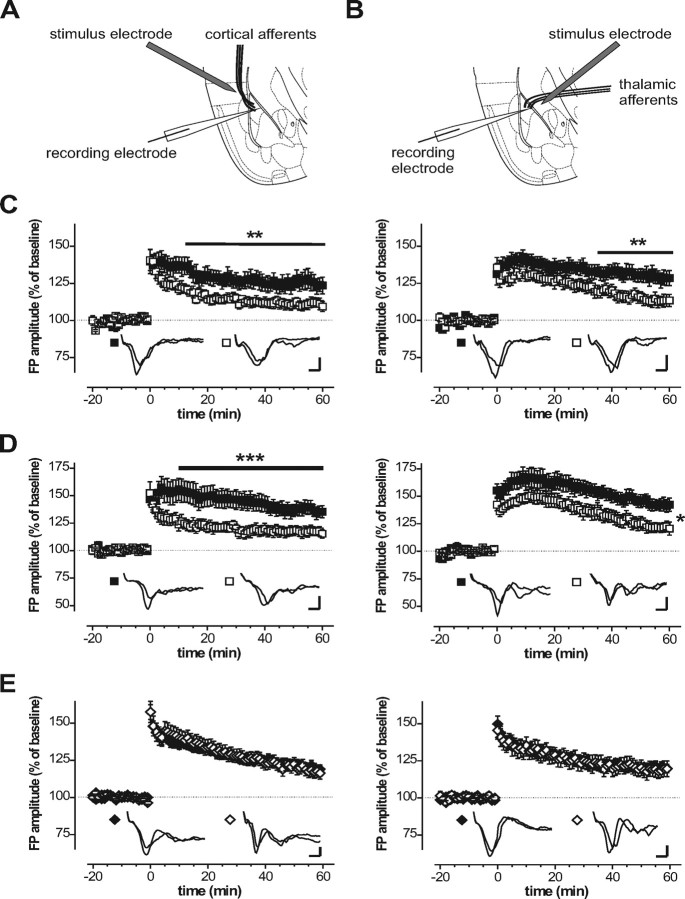
Figure 2.
LTP in the amygdala of transgenic mouse models lacking either cGKI or cGKII. Synaptic transmission was assessed by recording FPs in the lateral nucleus of the amygdala in response to stimulation of cortical (A) and thalamic (B) inputs, respectively. A strong tetanus (5 times for 1 s at 100 Hz with 90 s pause) was applied at time 0. Picrotoxin (50 μm) was present throughout recording. C, Time course of the FP evoked by stimulation of cortical (left) or thalamic (right) inputs recorded in brain slices from 4- to 5-week-old cGKI null mutants (□) and their litter-matched controls (■). D, Time course of the FP evoked by stimulation of cortical (left) or thalamic (right) inputs recorded in brain slices from 6- to 8-week-old cGKIα smooth muscle rescue mice (□) and their litter-matched controls (■). E, Time course of the FP evoked by stimulation of cortical (left) or thalamic (right) inputs recorded in brain slices from 6- to 8-week-old cGKII null mutants (◇) and their litter-matched controls (♦). The insets show representative FP recordings. Calibration: 2 ms, 250 μV. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005, respectively (ANOVA and Newman–Keuls post hoc test).